产品号 #100-0340_C
用于构建和维持人肠类器官的无血清的非条件培养基
若您需要咨询产品或有任何技术问题,请通过官方电话 400 885 9050 或邮箱 info.cn@stemcell.com 与我们联系。
用于构建和维持人肠类器官的无血清的非条件培养基
用于构建和维持人肠类器官的无血清的非条件培养基
IntestiCult™-SF 类器官生长培养基 (人)是一套完整的培养基,用于从人的肠隐窝高效地构建肠类器官并对其进行长期的维持培养。IntestiCult™-SF 是无血清且非条件培养基的配方。
肠类器官为研究肠道上皮提供了一个便捷的体外器官型培养系统。分离的肠隐窝在 IntestiCult™-SF 中培养时能快速形成复杂类器官。该类器官包含一个由具有极性的肠上皮细胞层包围而成的功能性腔体结构,细胞层中包含已知的成年肠上皮细胞类型。成熟的肠类器官会形成突出的芽体,与体内组织的肠隐窝结构相似。IntestiCult™-SF 支持患者活检样本中肠上皮干细胞的增殖,以及新鲜组织或现有冻存样本来源的类器官的扩增。
肠类器官培养的应用包括研究肠道上皮的发育和功能、构建肠道疾病模型,以及在肠道模型中筛选分子的有效性和毒性。肠类器官培养还可用于研究成体干细胞特性及再生治疗方法,并可通过 IntestiCult™ 类器官分化培养基 (人)(产品号 #100-0214)实现进一步分化。
欢迎通过我们的免费点播课程学习人肠类器官的培养方法,或浏览关于使用 IntestiCult™ 进行类器官培养流程的常见问题(FAQs)。此外,您还可以下载我们的电子书《Proven Protocols for Intestinal Organoid Culture: Getting Started with IntestiCult™》,获取肠类器官培养方案的精选合集。
如果您打算将此产品用于商业目的,请通过www.huborganoids.nl联系HUB以获得商业使用许可或有关HUB许可的说明。
分类
专用培养基
细胞类型
肠道细胞
种属
人
应用
类器官培养
品牌
IntestiCult
研究领域
疾病建模,药物发现和毒理检测,上皮细胞研究,类器官,干细胞生物学
制剂类别
无血清
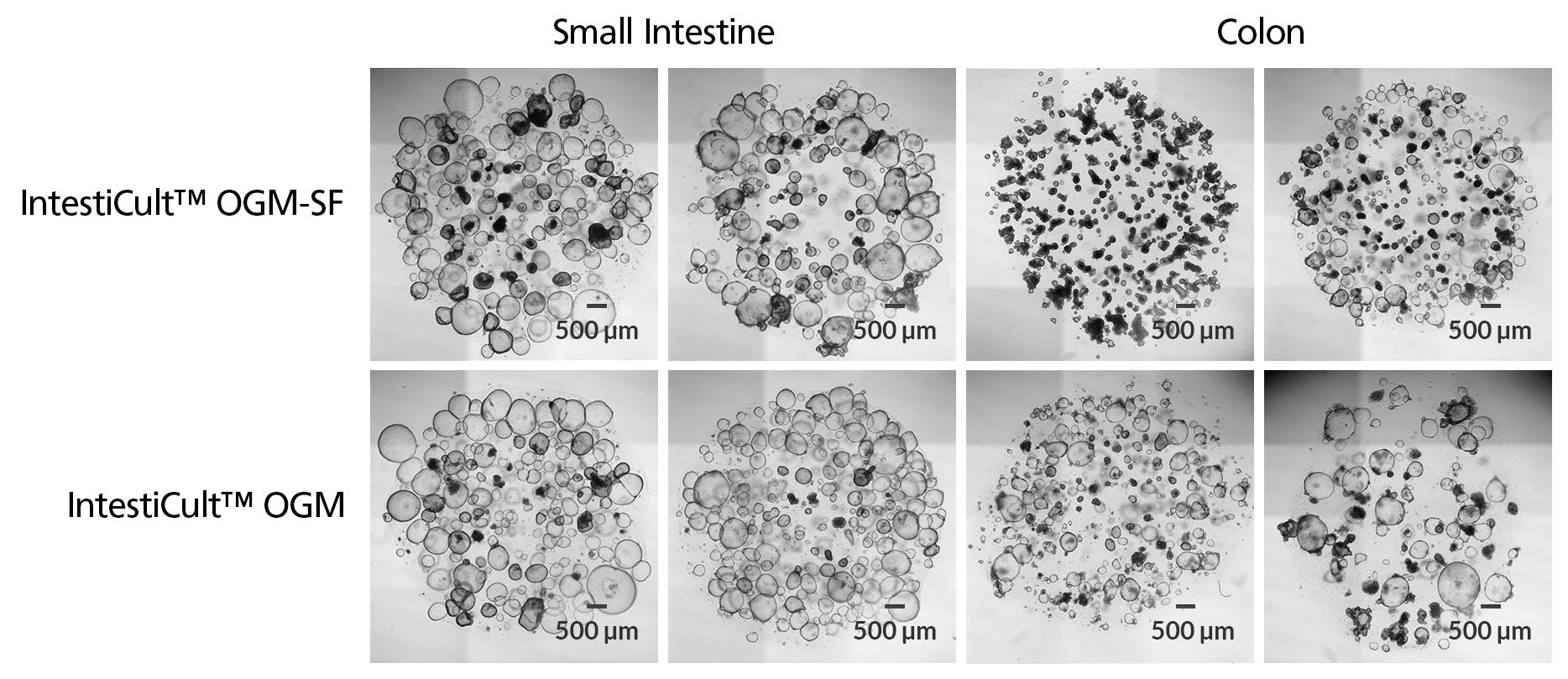
Figure 1. Organoids Grown in IntestiCult™-SF Have a Comparable Morphology to Organoids Grown in IntestiCult Organoid Growth Medium (Human)
Human intestinal organoids grown in IntestiCult™-SF and IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human) display similar morphological characteristics during organoid maintenance and expansion. Shown are organoids from small intestinal and colonic tissues, established and expanded in IntestiCult™-SF or IntestiCult™ OGMH. Organoids are imaged at passage 5 of culture for all images. Scale bars = 500 μm.
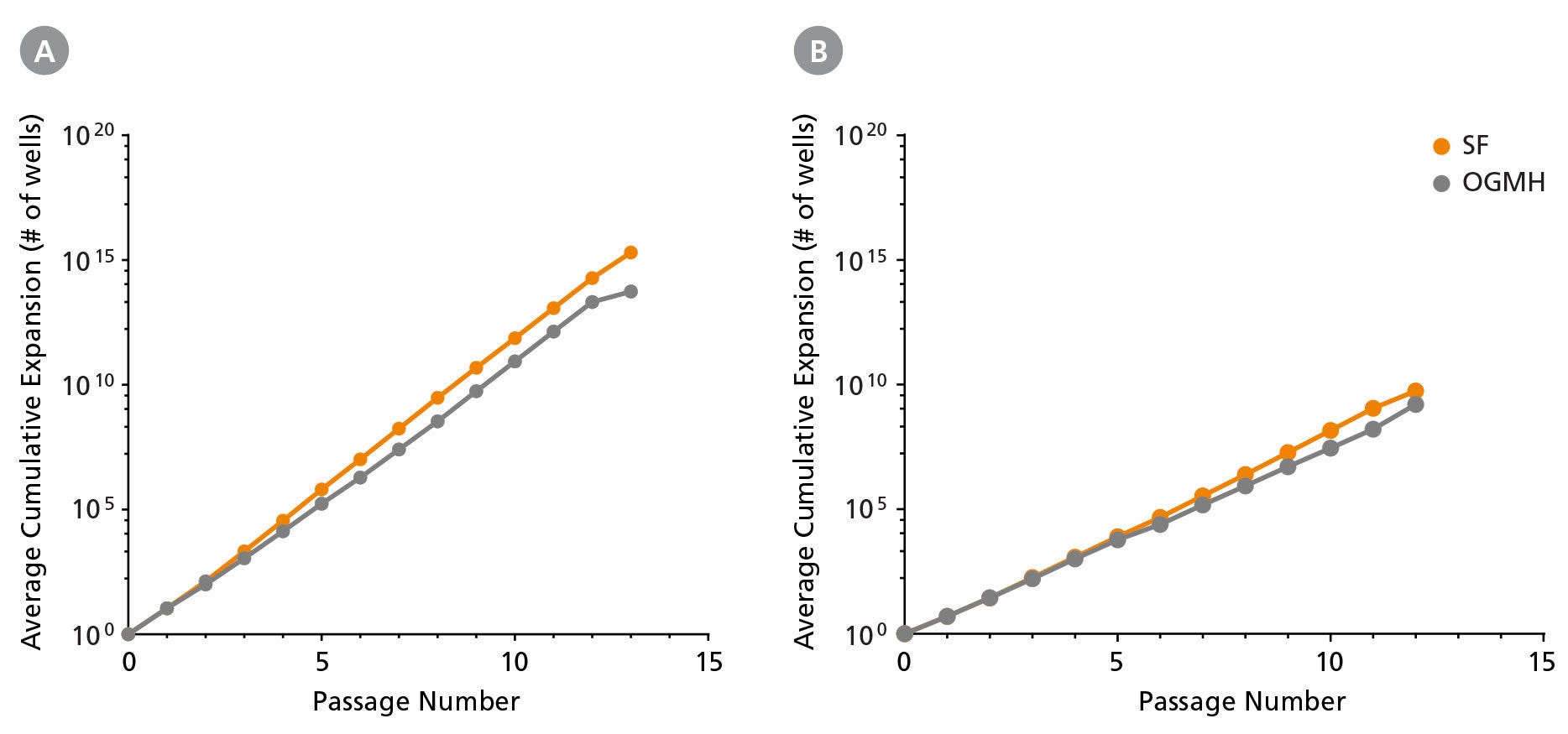
Figure 2. IntestiCult™-SF Provides More Efficient Expansion of Intestinal Organoids Compared to IntestiCult™ OGMH
Human intestinal organoids established from both (A) small intestinal and (B) colonic tissues display more efficient expansion during extended culture when grown in IntestiCult™-SF compared to those grown in IntestiCult™ OGMH. Shown is the cumulative expansion of organoids averaged across two separate donor lines in each medium. IntestiCult™-SF demonstrates more efficient expansion of both small intestinal and colonic organoids during extended culture.
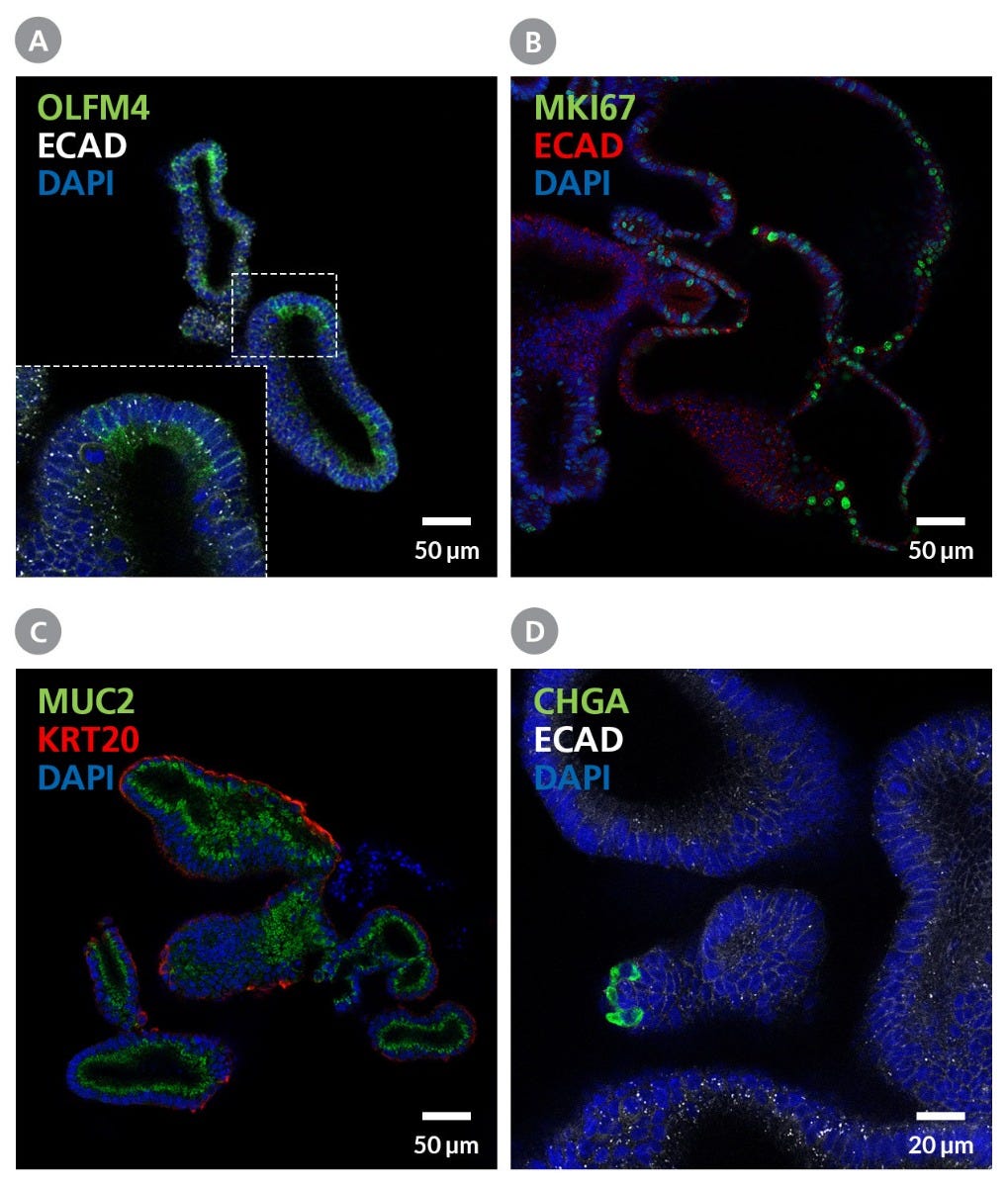
Figure 3. Organoids Grown in IntestiCult™-SF Display Some Characteristics of the Mature Intestinal Epithelium
While organoids grown in IntestiCult™-SF display a primarily "immature" phenotype including expression of (A) intestinal stem cell marker OLFM4 and (B) proliferation marker ki67. (C, D) These organoids also display some characteristics of the mature epithelium such as the presence of goblet cells (C, Muc2), enterocytes (C, KRT20), and enteroendocrine cells (D, CHGA). Scale bars = 50 μm or 20 μm as indicated.
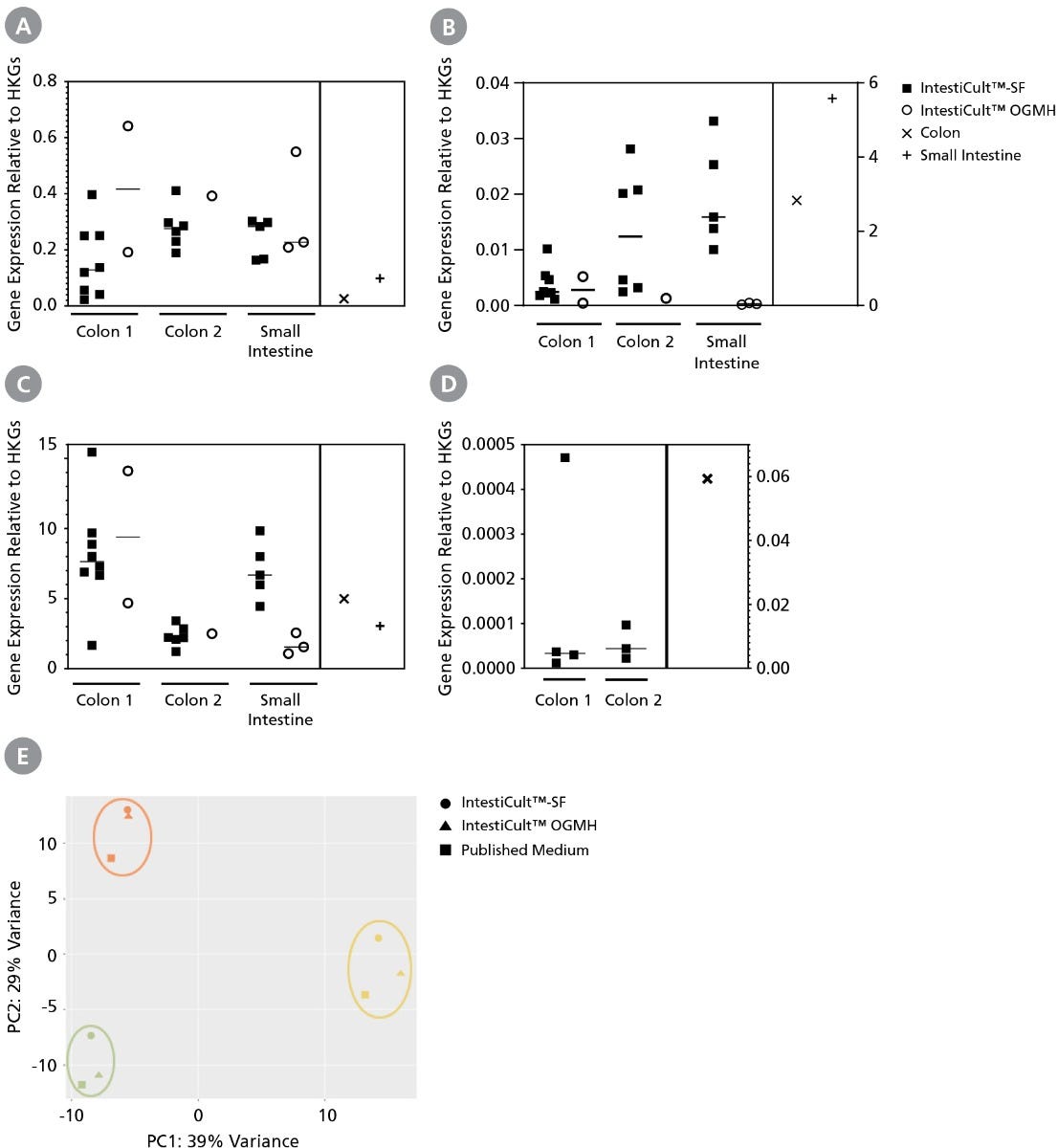
Figure 4. Organoids Grown in IntestiCult™-SF Display Similar Genetic Expression Profiles to Those Grown in IntestiCult™ OGMH
Analysis of intestinal organoids grown in IntestiCult™-SF by qPCR of (A) Lgr5, (B) Muc2, (C) Krt20, and (D) ChgA demonstrates similar genetic expression profiles to those grown in IntestiCult™ OGMH, as well as to colonic and small intestinal tissue (A-D; x and + respectively). All expression levels are shown relative to ACTB and TBP house-keeping genes (HKGs). (E) Further analysis of three separate donors grown in IntestiCult™-SF (circles) IntestiCult™ OGMH (triangles), and published medium (squares) by principle component analysis demonstrates that differences between cultures are primarily due to donor variability with samples forming distinct clusters separated by donor, rather than by medium.
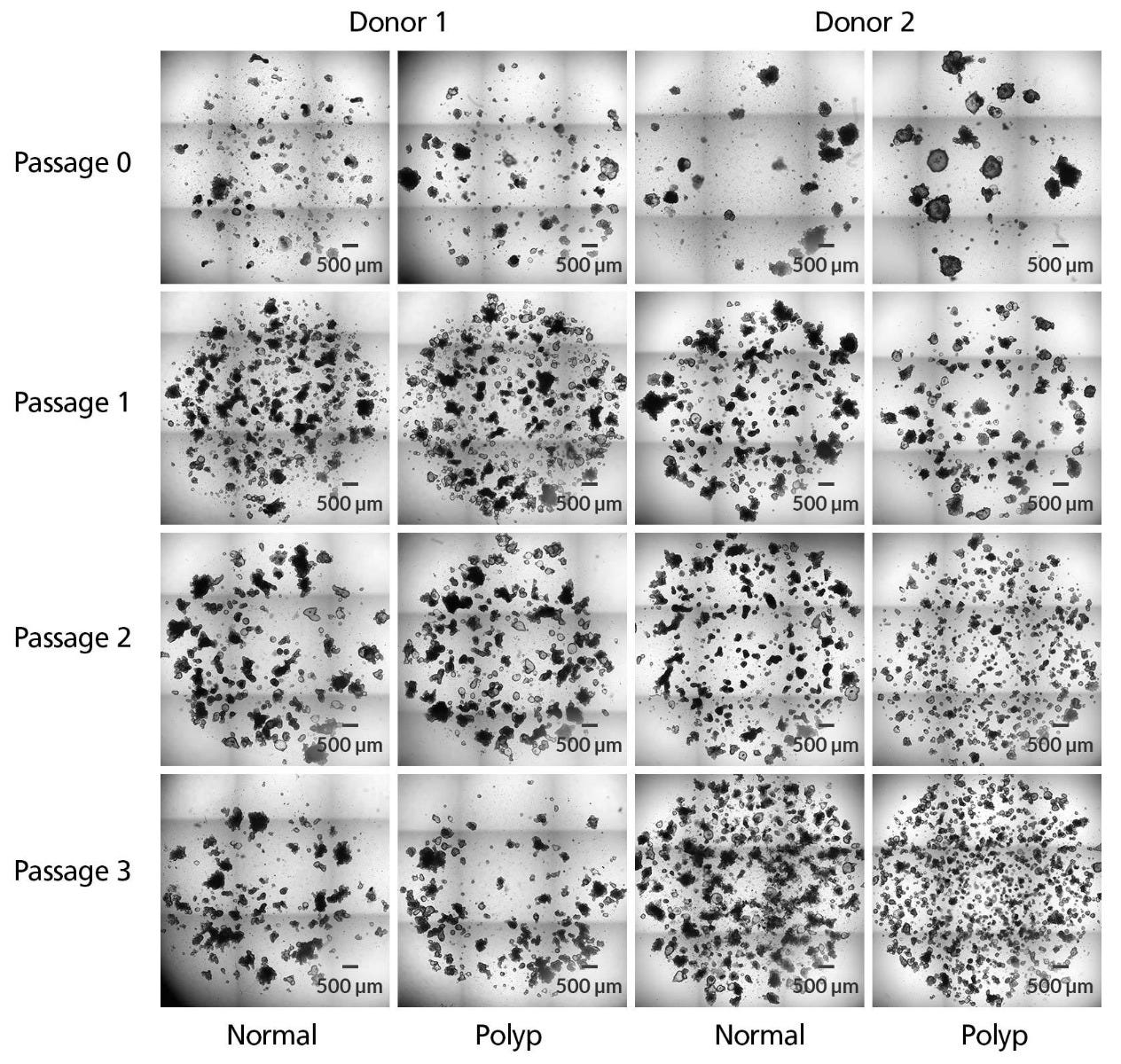
Figure 5. IntestiCult™-SF Enables Efficient Expansion of Intestinal Organoids from Polyp Tissue
Intestinal organoids were established from both normal epithelial tissue, as well as from polyp tissue, and expanded for three passages in IntestiCult™-SF. Shown are cultures from two separate donors, imaged at the end of each passage immediately before passaging.
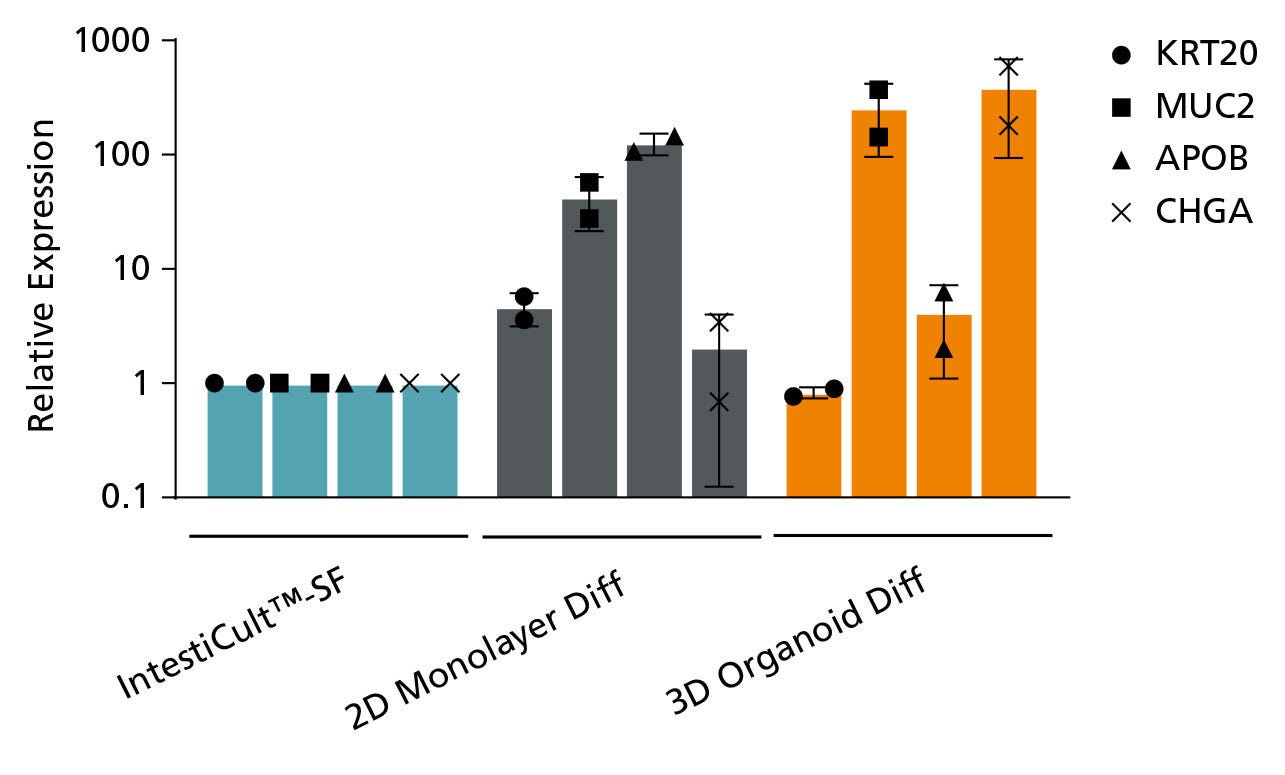
Figure 6. Organoids Grown in IntestiCult™-SF can be Further Differentiated using IntestiCult™ Organoid Differentiation Medium
Further differentiation of organoids in IntestiCult™-SF can be achieved by passaging organoid cultures in IntestiCult™ Organoid Differentiation Medium as organoid-derived monolayers (2D Monolayer Diff) or in 3D organoid culture (3D Organoid Diff). Upon differentiation, markers for enterocytes (KRT20, ApoB), goblet cells (Muc2), and enteroendocrine cells (ChgA) are upregulated compared to organoids grown in IntestiCult™-SF.
请在《产品说明书》中查找相关支持信息和使用说明,或浏览下方更多实验方案。
本产品专为以下研究领域设计,适用于工作流程中的高亮阶段。探索这些工作流程,了解更多我们为各研究领域提供的其他配套产品。
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
| 物种 | 人类 |
|---|---|
| 配方 | 无血清 |
用于将人肠道类器官在3D,或在单层/气液界面培养的形式下进一步分化的培养基
杜氏磷酸盐缓冲液,不含钙和镁离子
用于细胞分离和细胞培养的无菌聚丙烯锥形管
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。
在线联系