产品号 #100-0528_C
用于hPSC衍生的分支肺类器官成熟的无血清培养基
若您需要咨询产品或有任何技术问题,请通过官方电话 400 885 9050 或邮箱 info.cn@stemcell.com 与我们联系。
使用STEMdiff™分支肺类器官成熟试剂盒,在长期(>28天)培养中成熟和维持人类分支肺类器官。
无血清的STEMdiff™分支肺类器官成熟试剂盒可用于可重复地成熟人类胚胎干细胞(ES)和诱导多能干细胞(iPS)衍生的肺芽类器官 。所得类器官将形成近端和远端样分支气道上皮结构,表达EPCAM、NKX2.1、SOX2、SOX9、MUC1和P63等标志物。在Matrigel®夹层培养体系中维持超过28天后,成熟肺细胞标志物(如SFTPC、SFTPB和ABCA3)的表达水平会显著提高 。
有关使用 STEMdiff™ 分支肺类器官培养基系统启动和成熟分支肺类器官的方案的详细信息,请参阅产品信息表 (PIS)。
分类
专用培养基
细胞类型
上皮细胞,PSC衍生,间充质细胞,PSC衍生,多能干细胞
种属
人
应用
分化,基因组编辑,类器官培养
品牌
STEMdiff
研究领域
疾病建模,药物发现和毒理检测,感染性疾病(传染病),呼吸系统研究,移植研究
制剂类别
无血清
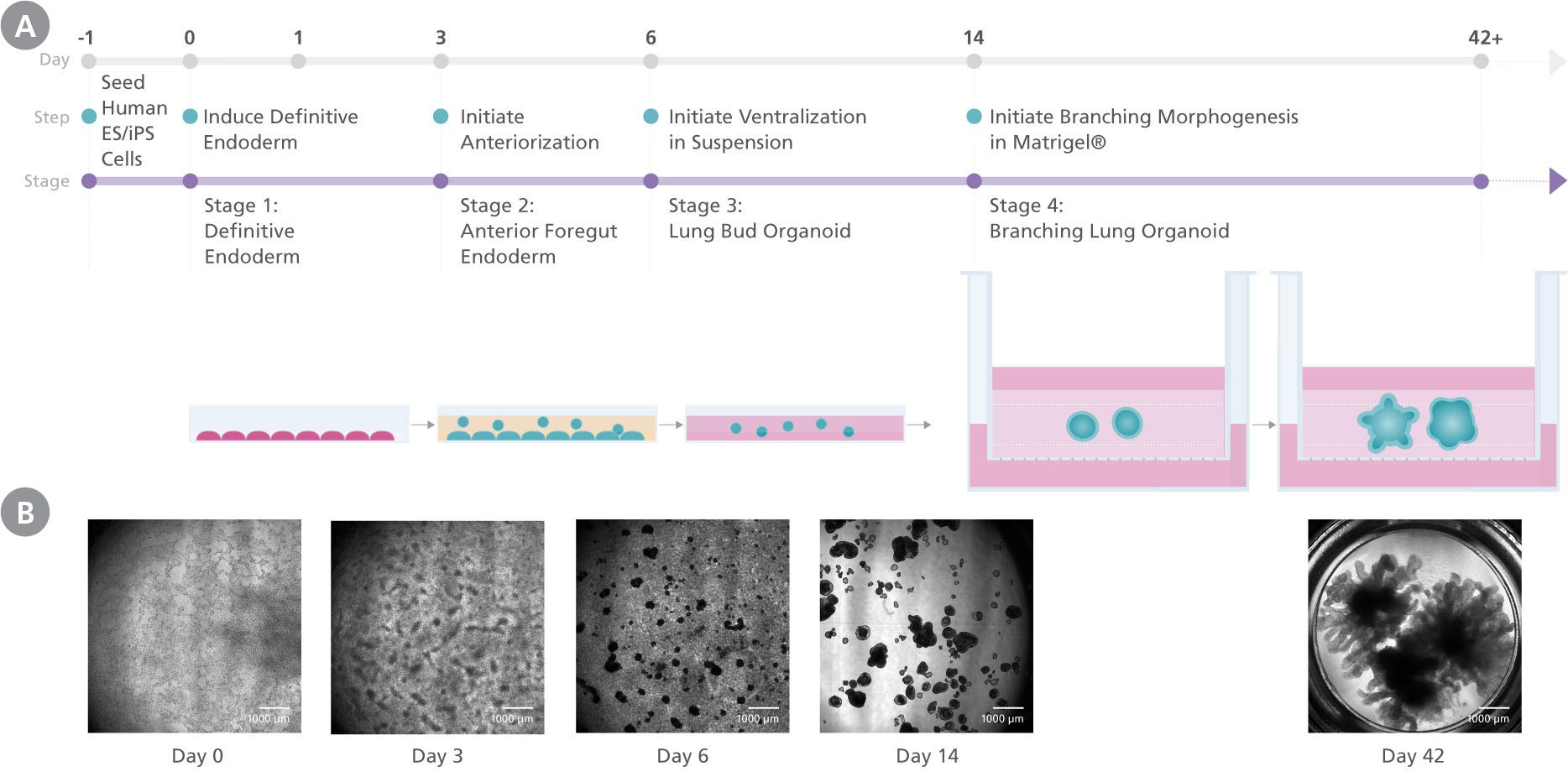
Figure 1. Generation Of Branching Lung Organoids Using the STEMdiff™ Branching Lung Organoid Kit
(A) Human PSC cultures progress through a four-stage differentiation process to generate human branching lung organoids. By the end of stage 1 (day 3), cultures exhibit characteristics typical of definitive endoderm and anterior foregut differentiation is initiated. During stage 2 (days 3 - 6) anterior foregut endoderm buds are released from the monolayer, and are then suspended to form ventralized lung bud organoids in stage 3 (days 6 - 14). In stage 4, the lung bud organoids are embedded into Matrigel sandwich cultures to mature into branching lung organoids. (B) Morphological representation of the culture at different stages.
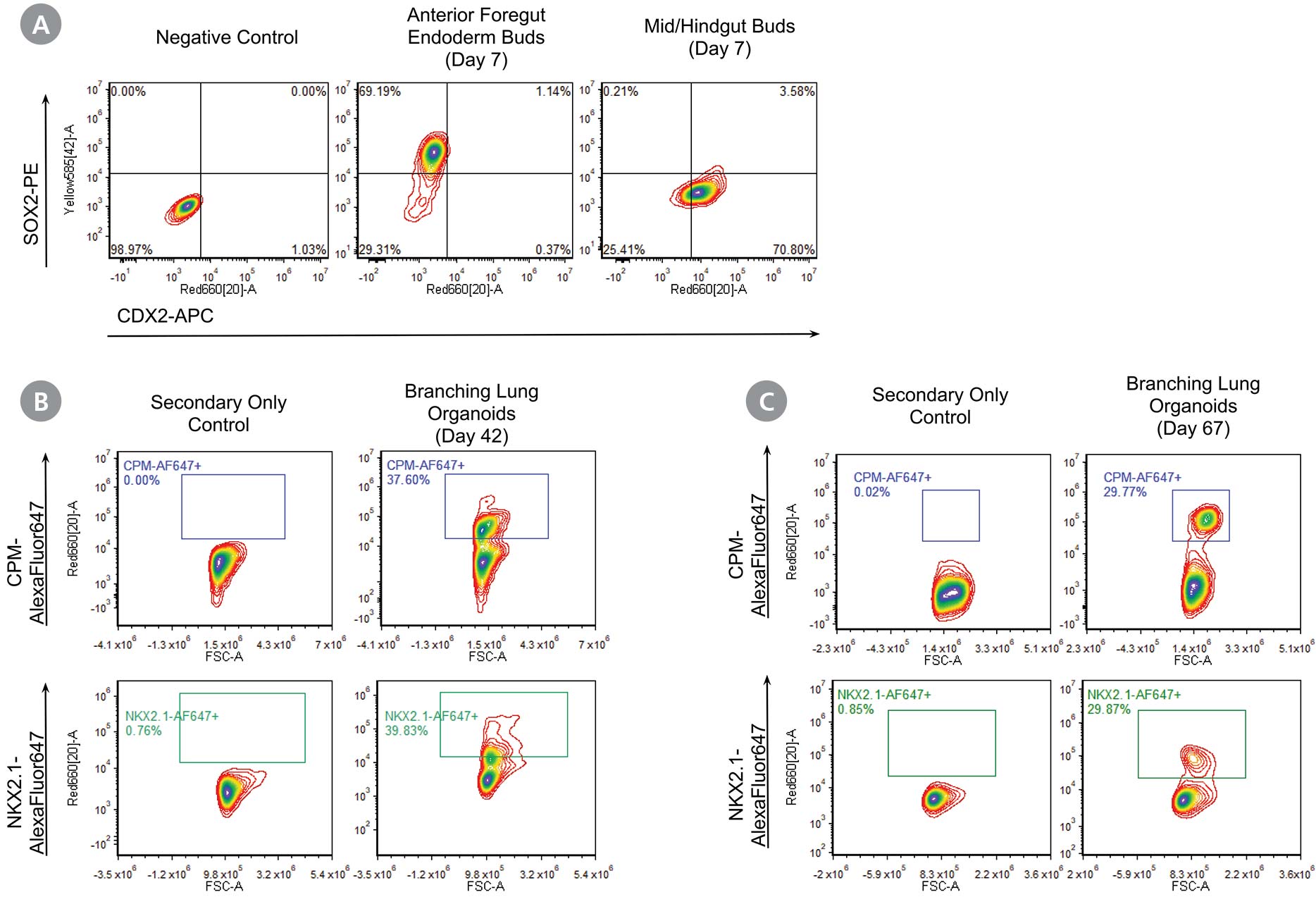
Figure 2. STEMdiff™ Branching Lung Organoid Kit Supports Expression of Key Lung Markers at Different Stages
Flow cytometric analysis at different stages of the STEMdiff™ Branching Lung Organoid Kit workflow shows protein expression of key lung markers. (A) Anterior foregut endoderm (AFE) buds generated at the end of stage 2 demonstrates high expression of the anterior foregut marker, SOX2 and absence of mid/hindgut marker, CDX2. (B) Cells from branching lung organoids on day 42 (stage 4) express lung progenitor marker NKX2.1 and its surrogate cell surface marker CPM. (C) NKX2.1 and CPM expression are maintained in long-term cultures as seen by flow cytometric analysis of cells from branching lung organoids (day 67).
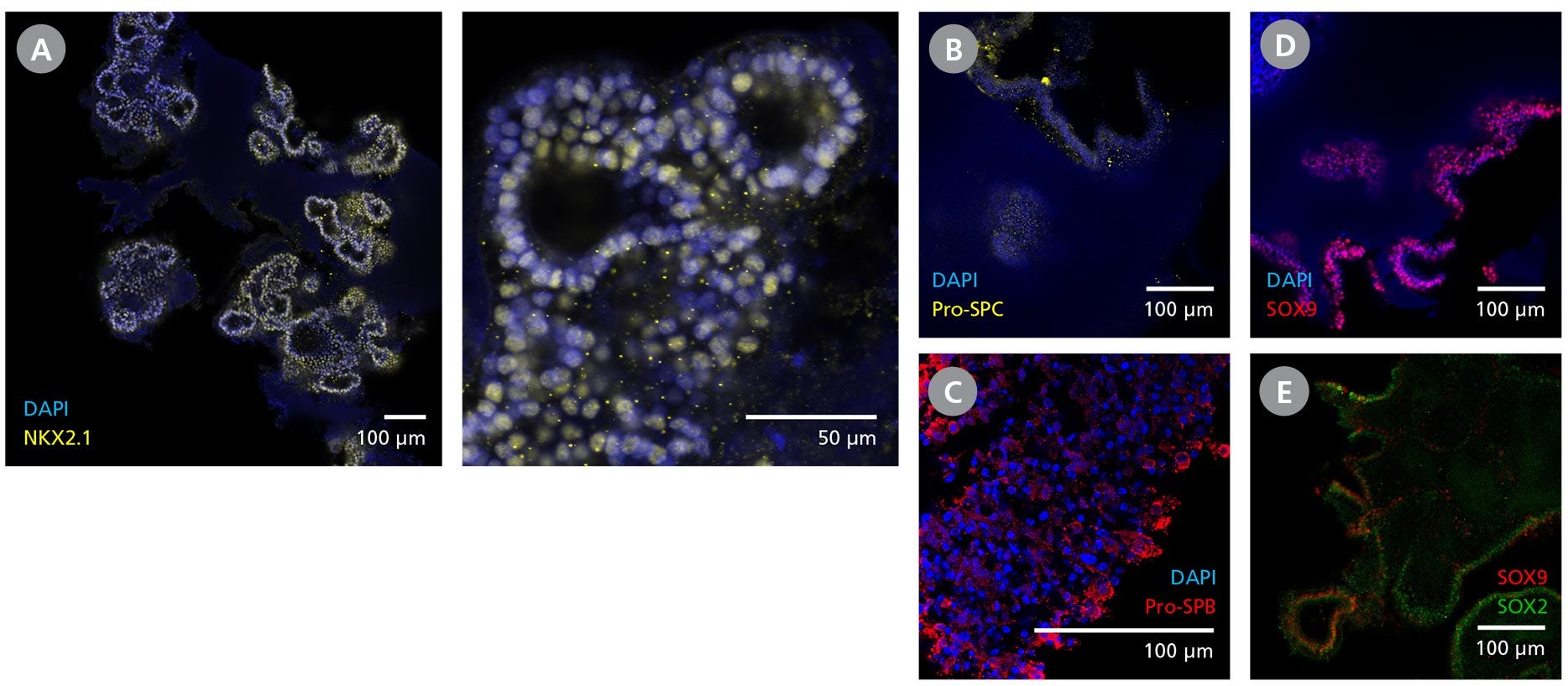
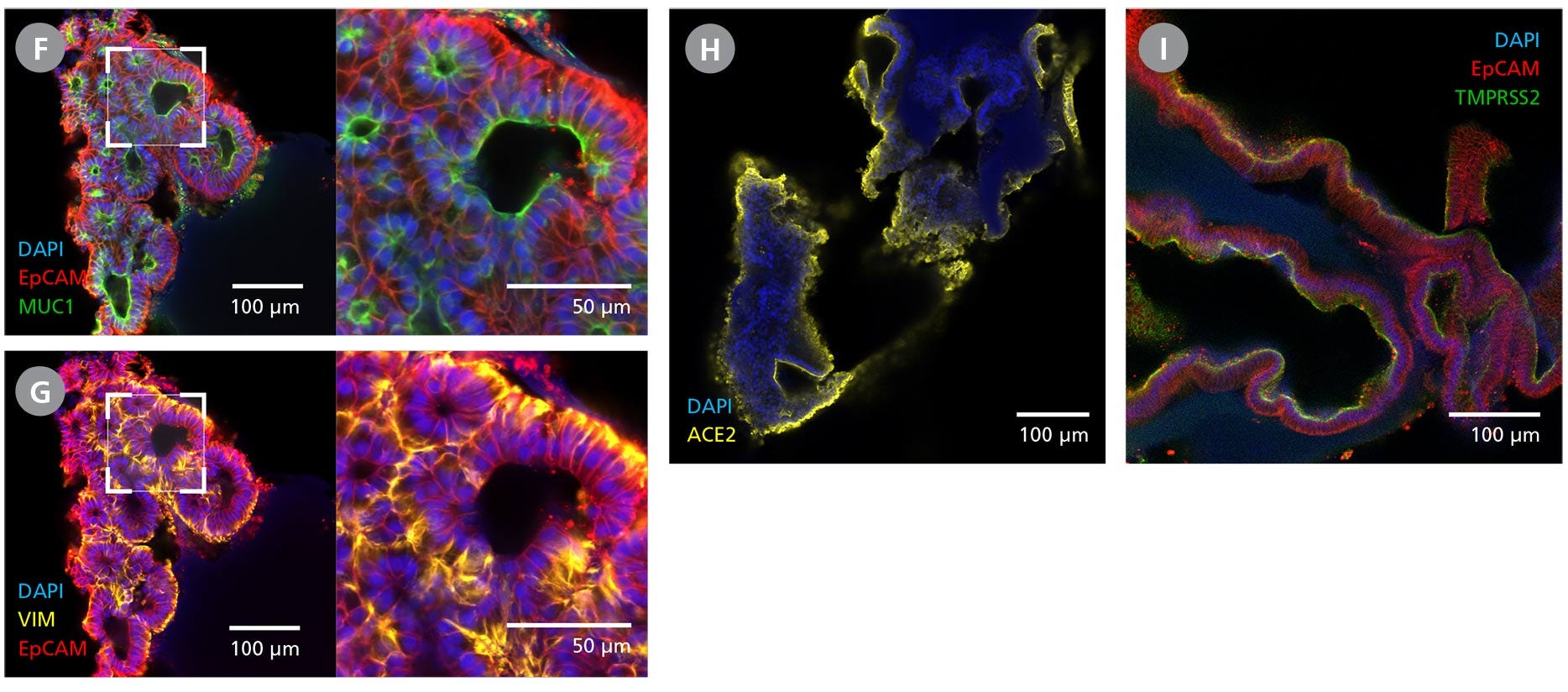
Figure 3. Branching Lung Organoids Cultured in STEMdiff™ Branching Lung Organoid Kit Feature Key Protein Markers and Exhibit Branching Morphogenesis
(A) Branching lung organoids express lung progenitor marker NKX2.1 throughout their branching structures, and (B, C) demonstrate the presence of alveolar type II-like cells with Pro-surfactant protein B and C expressions. (D, E) These organoids undergo proximodistal differentiation demonstrated by the differential expression of SOX2 and SOX9. (F) MUC1 can be found luminally expressed while the (G) organoids are surrounded by VIM-expressing mesenchyme. (H, I) Branching lung organoids generated in STEMdiff™ Branching Lung Organoid Kit also express proteins associated with SARS-CoV-2 entry, ACE2 and TMPRSS2. Protein expression was visualized by immunohistochemistry and confocal microscopy of branching lung organoids on day 63.
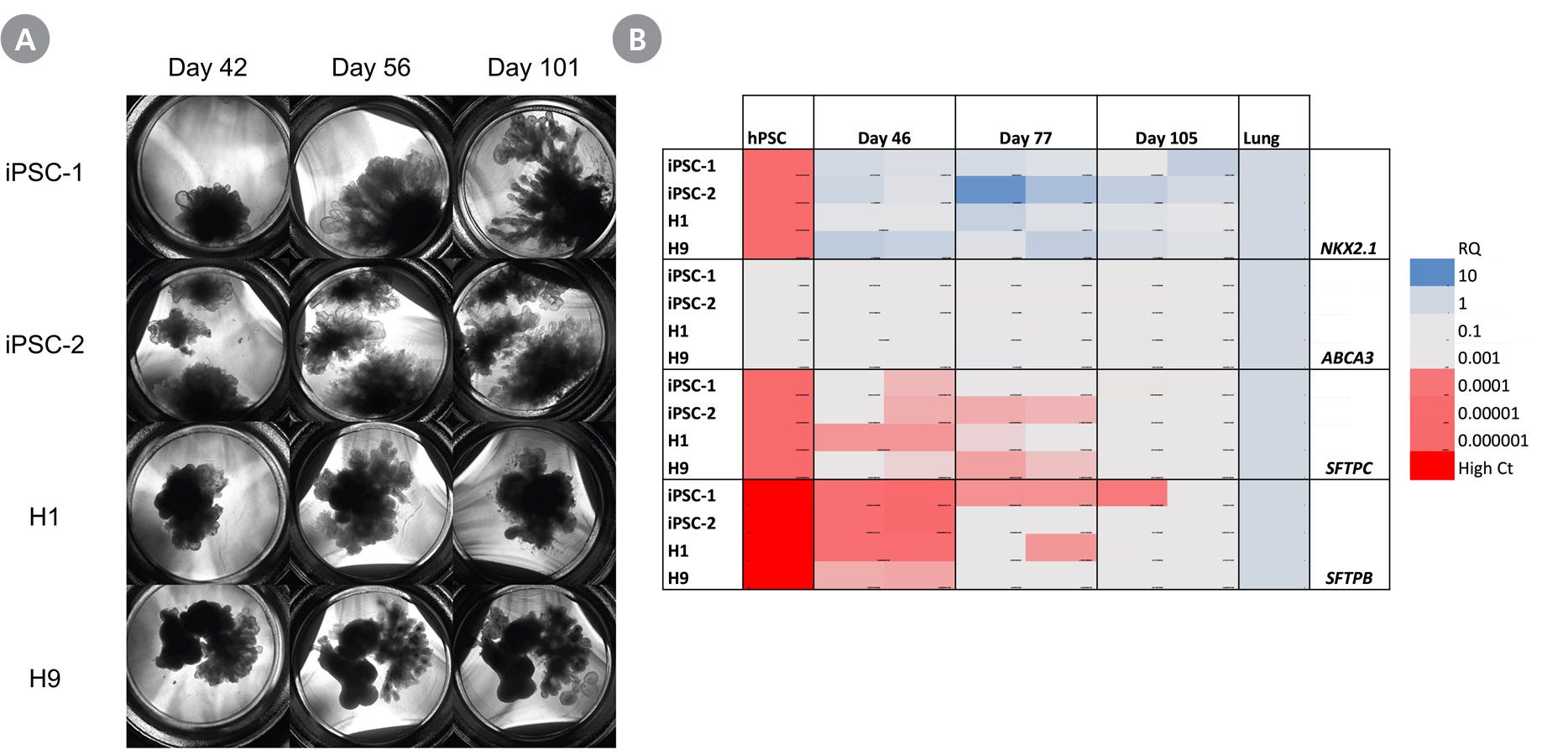
Figure 4. Branching Lung Organoids Cultured in STEMdiff™ Branching Lung Organoid Maturation Kit For Extended Periods Express More Mature Lung Markers
(A) The branching tips of branching lung organoids derived from peripheral blood endothelial progenitor cell-derived iPS cells (iPSC-1), peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived iPS cells (iPSC-2) or embryonic stem cells (H1 and H9) continue to grow and branch up to day 101. (B) The expression levels of more mature distal lung markers ABCA3, SFTPC, and SFTPB increase overtime. Morphology and gene expression of branching lung organoids cultured up to day 105 were assessed by RT-qPCR. RQ-values were normalized to TBP and compared to commercially available lung RNA.
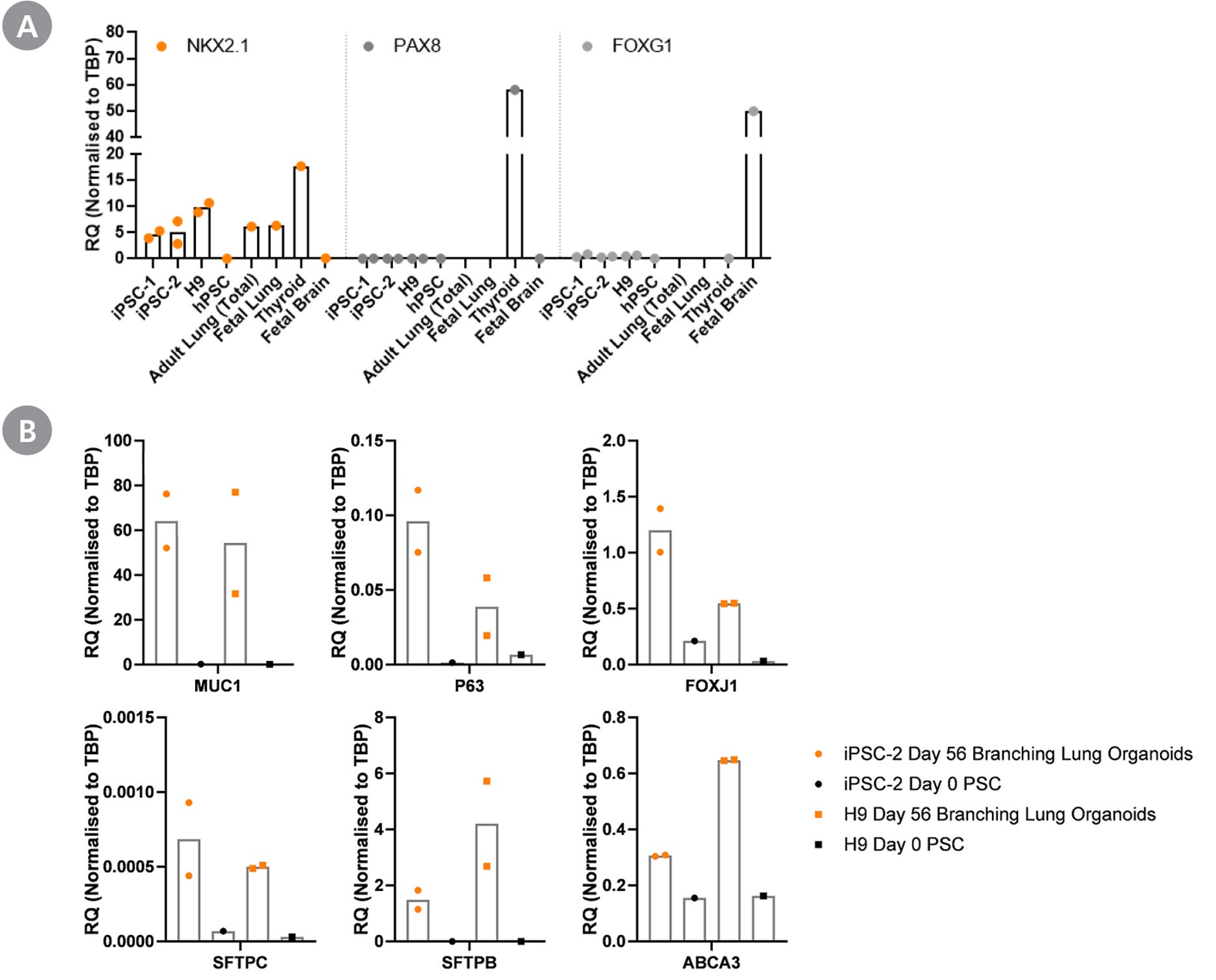
Figure 5. Branching Lung Organoid Cells Are Specifically Differentiated Towards the Lung
Gene expression profile of branching lung organoids (day 42+) analysed by RT-qPCR show presence of key lung markers and absence of off-target markers. Branching lung organoids at day 42 express (A) lung-thyroid-forebrain marker NKX2.1 and does not exhibit thyroid marker PAX8 and forebrain marker FOXG1. (B) The expressions of proximal lung markers MUC1, P63, and FOXJ1 and distal lung markers SFTPC, SFTPB, and ABCA3 are upregulated in day 56 branching lung organoids, when compared to respective pluripotent stem cells (PSCs). All expression levels are normalized to the housekeeping gene TBP. iPSC-1: peripheral blood endothelial progenitor cell-derived iPS cells; iPSC-2: peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived iPS cells.
请在《产品说明书》中查找相关支持信息和使用说明,或浏览下方更多实验方案。
本产品专为以下研究领域设计,适用于工作流程中的高亮阶段。探索这些工作流程,了解更多我们为各研究领域提供的其他配套产品。
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。
在线联系