产品号 #100-0170_C
用于hPSC向NK细胞的扩增和分化
若您需要咨询产品或有任何技术问题,请通过官方电话 400 885 9050 或邮箱 info.cn@stemcell.com 与我们联系。
用于hPSC向NK细胞的扩增和分化
使用无饲养层、无血清的STEMdiff™ NK 细胞分化试剂盒将人多能干细胞(hPSCs)分化为NK细胞
STEMdiff™ NK细胞分化试剂盒方案首先采用无动物成分的STEMdiff™造血分化 - EB试剂,从hPSCs生成拟胚体(EBs),随后进一步分化为CD34+细胞。本试剂盒包含该步骤所需全部EB试剂:
• STEMdiff™造血分化 - EB基础培养基
• STEMdiff™造血分化 - EB补充剂 A
• STEMdiff™造血分化 - EB补充剂 B
随后使用StemSpan™试剂将CD34+细胞进一步定向分化为CD56+ NK细胞:
• StemSpan™ SFEM II
• StemSpan™淋系祖细胞扩增补充剂(10X)
• StemSpan™淋系分化包被材料(100X)
• StemSpan™ NK细胞分化补充剂(100X)
为方便使用,试剂盒内所有STEMdiff™造血分化 - EB及StemSpan™试剂均可单独购买
分类
专用培养基,添加剂
细胞类型
造血细胞,PSC衍生,NK 细胞,多能干细胞
种属
人
应用
细胞培养,分化,扩增
品牌
STEMdiff
研究领域
癌症,疾病建模,免疫,干细胞生物学
制剂类别
无血清
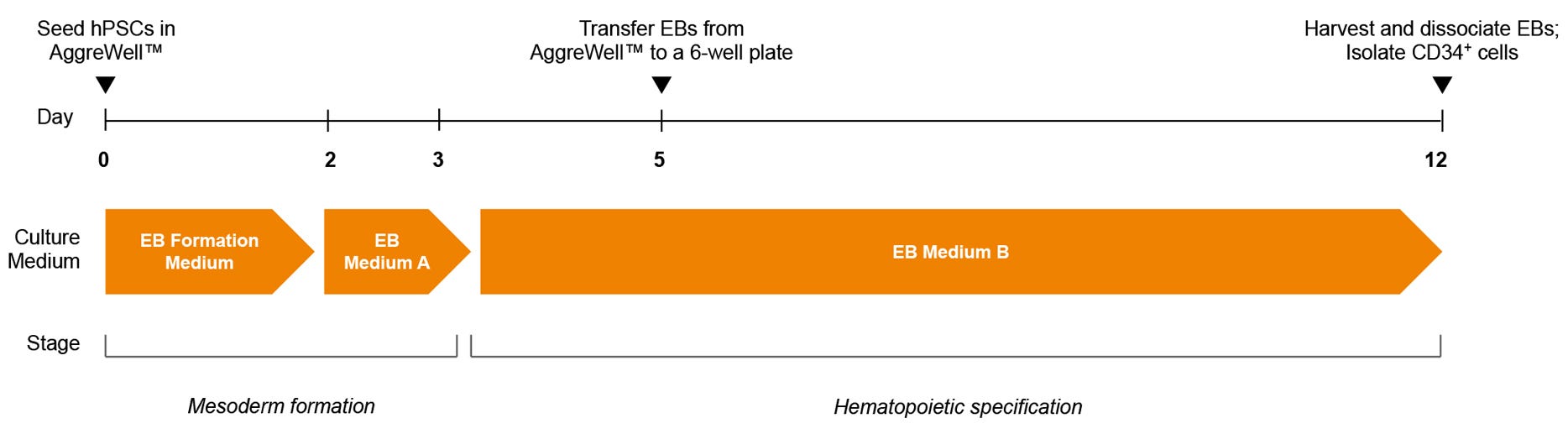
Figure 1. STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic-EB Progenitor Differentiation Protocol
hPSCs are harvested and dissociated into a single-cell suspension prior to seeding into AggreWell™ plates in EB Formation Medium (EB Medium A + 10 µM Y-27632) to form 600-cell aggregates. A half-medium change with EB Medium A is performed on day 2. After a total of 3 days of mesoderm formation, the medium is changed to EB Medium B to induce hematopoietic lineage differentiation. On day 5, EBs are transferred onto non-tissue culture-treated plates. After a total of 12 days, EBs are harvested and dissociated, then CD34+ cells are enriched by EasySep™ positive selection.
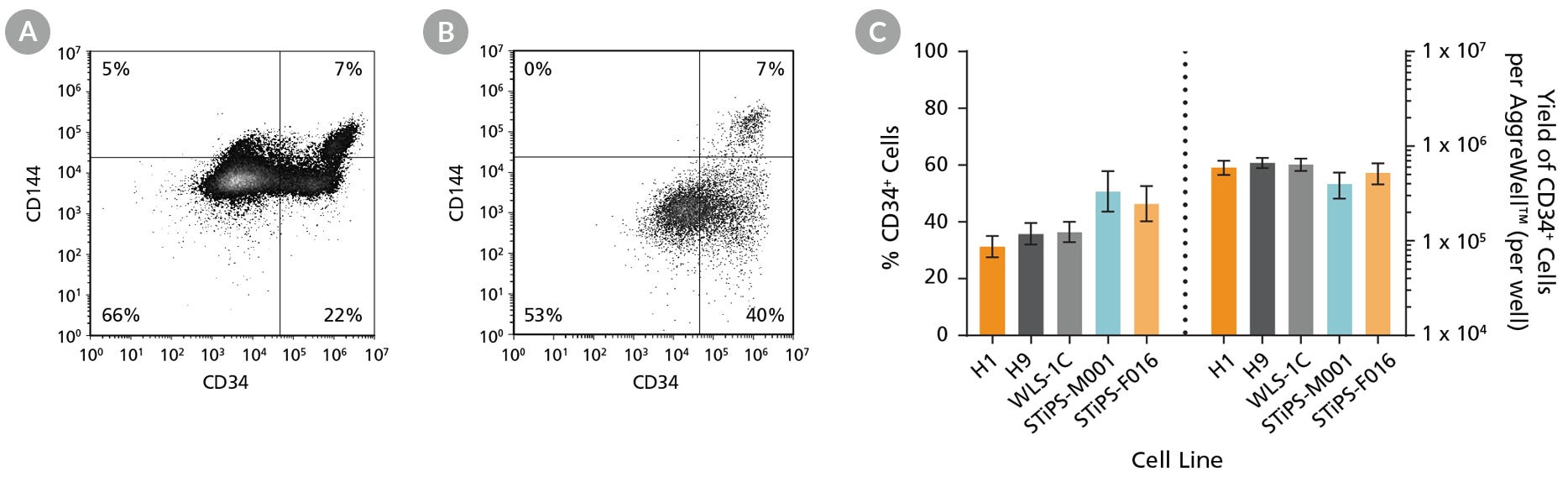
Figure 2. hPSCs Differentiate to CD34+ Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells After 12 Days of Culture
Human ES and iPS cells were induced to differentiate to CD34+ cells using the 12-day protocol shown in Figure 1. At the end of the culture period, cells were harvested, dissociated into a single-cell suspension, and analyzed by flow cytometry for CD34 and CD144 expression. Dead cells were excluded by light-scatter profile and DRAQ7™ staining. Representative flow cytometry plots for (A) ES (H1) cell-derived and (B) iPS (STiPS-M001) cell-derived cells analyzed on day 12 are shown. (C) The average frequency of viable CD34+ cells on day 12 (before CD34+ cell isolation) for two ES cell lines (H1 and H9) and three iPS cell lines (WLS-1C, STiPS-M001, and STiPS-F016) ranged between 31% and 51%. The average yield of CD34+ cells produced per well of a 6-well AggreWell™400 plate ranged between 4.0 x 105 and 6.7 x 105. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 9 - 35).
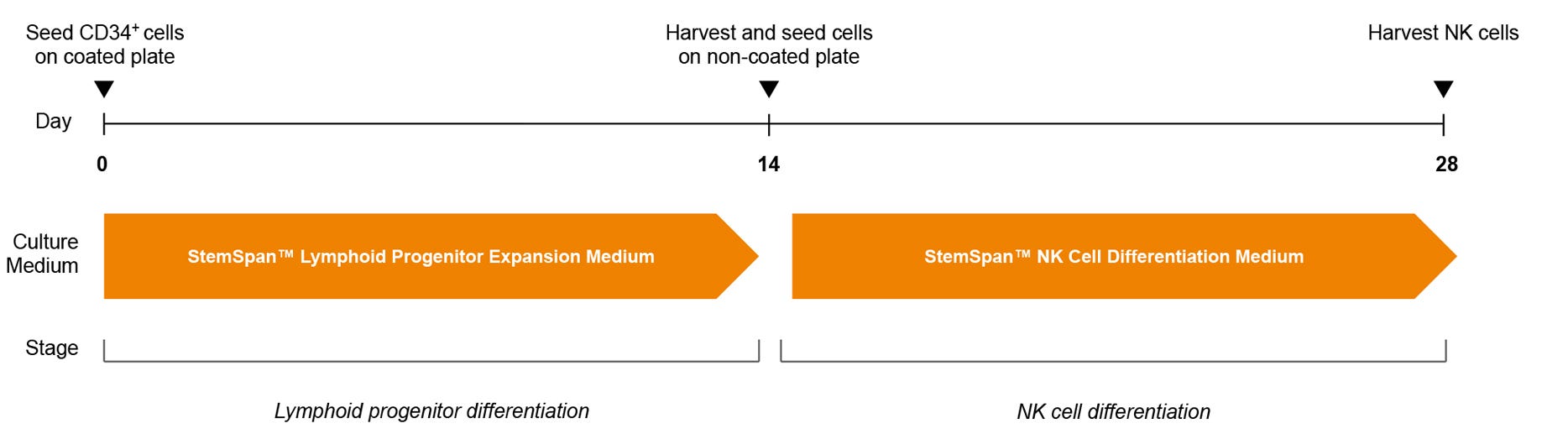
Figure 3. NK Cell Generation Protocol
hPSC-derived CD34+ cells are seeded in StemSpan™ Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Medium on plates coated with StemSpan™ Lymphoid Differentiation Coating Material. On day 14, cells at the lymphoid progenitor stage are harvested and reseeded in StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Medium onto non-coated plates for further differentiation to NK cells.
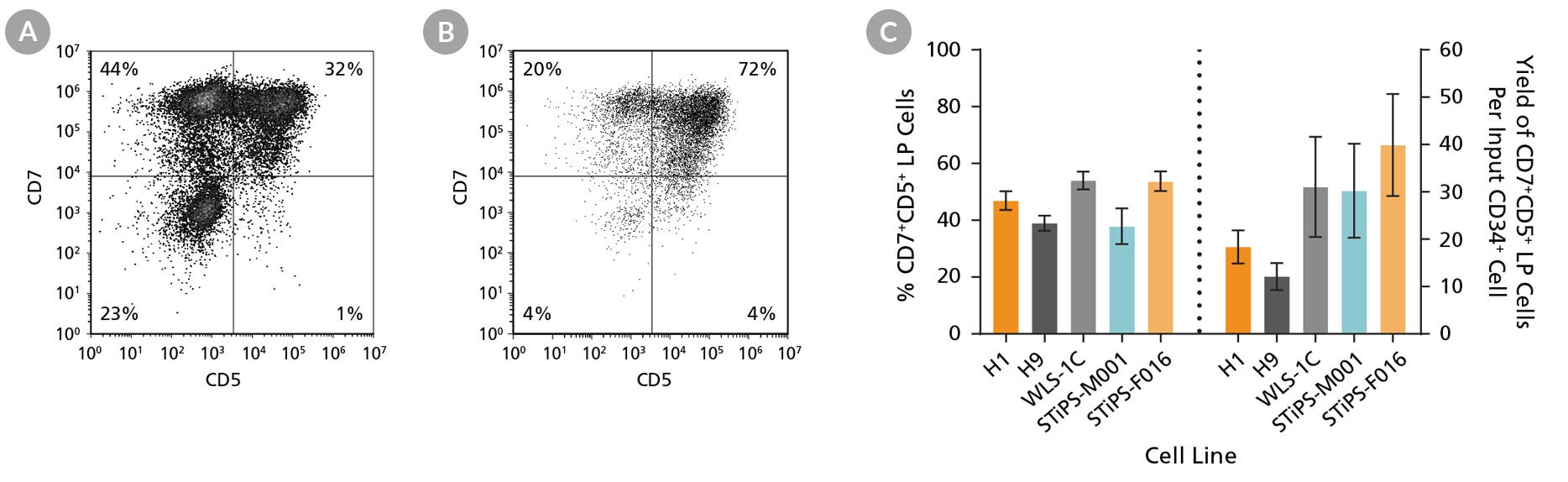
Figure 4. hPSC-Derived CD34+ Cells Differentiate to CD5+CD7+ Lymphoid Progenitor Cells Over 14 Days of Culture
hPSC-derived CD34+ cells were cultured for 14 days in StemSpan™ Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Medium on plates coated with StemSpan™ Lymphoid Differentiation Coating Material (Figure 2). Cells were harvested and analyzed for CD7 and CD5 expression by flow cytometry. Representative flow cytometry plots for (A) ES (H1) cell-derived and (B) iPS (STiPS-M001) cell-derived cells are shown. (C) The average frequency of viable CD7+CD5+ lymphoid progenitor cells on day 14 ranged between 38% and 54%, and the average yield of lymphoid progenitor cells produced per input hPSC-derived CD34+ cell was between 12 and 40. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 8 - 32).
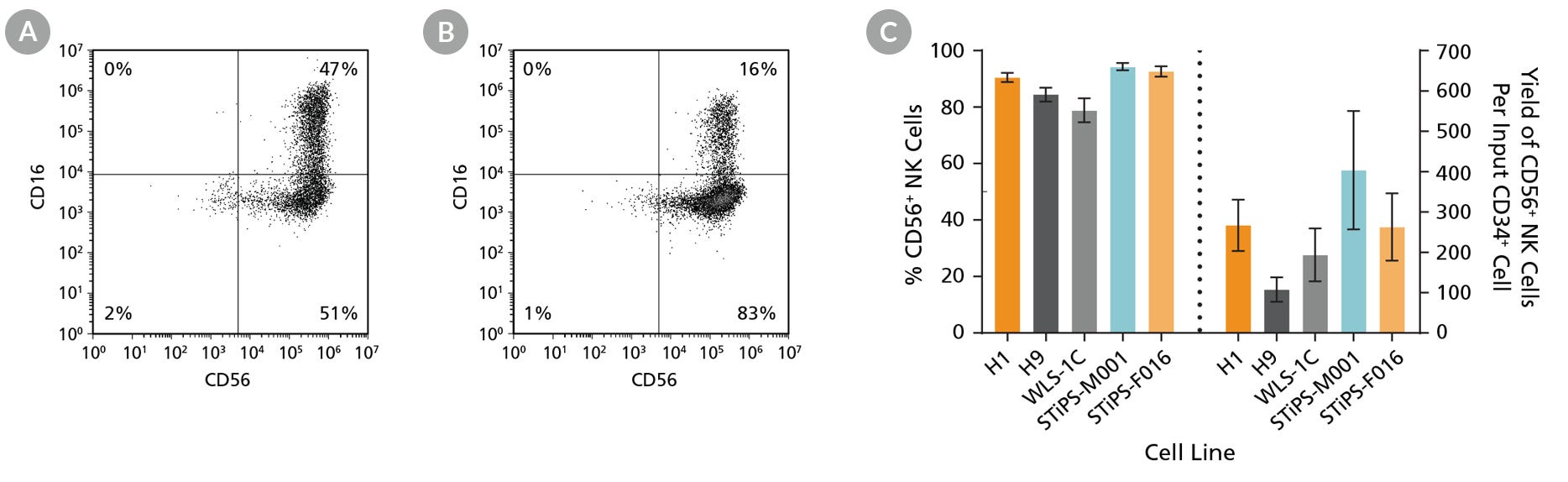
Figure 5. hPSC-Derived Lymphoid Progenitor Cells Differentiate to CD56+ NK Cells After 14 Days of Culture
hPSC-derived lymphoid progenitor cells were cultured in StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Medium on non-coated plates for 14 days (Figure 2). Cells were harvested and analyzed for expression of CD56 and CD16 by flow cytometry. Representative flow cytometry plots are shown for both (A) ES (H1) cell-derived and (B) iPS (STiPS-M001) cell-derived cells. (C) After 28 days of culture, the average frequency of viable CD56+ NK cells from hPSC-derived CD34+ cells ranged between 79% and 94%. The average yield of CD56+ cells produced per hPSC-derived CD34+ cell was between 108 and 404. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 7 - 18).
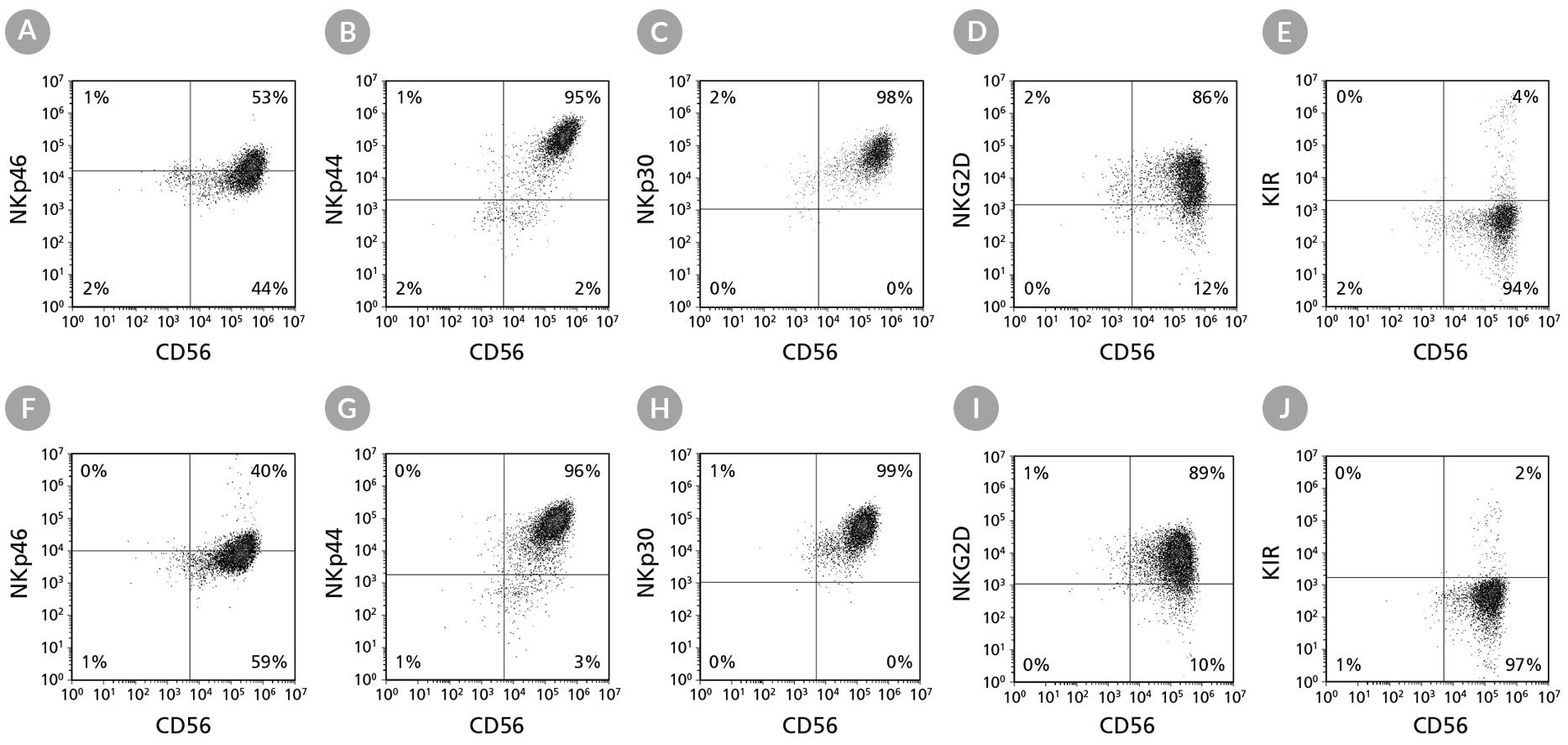
Figure 6. Cell Surface Marker Expression on PSC-Derived CD56+ NK Cells After 28 Days of Culture
hPSC-derived CD34+ cells were cultured in StemSpan™ Lymphoid Progenitor Expansion Medium on plates coated with StemSpan™ Lymphoid Differentiation Coating Material for 14 days, followed by 14 days of culture in StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Medium on non-coated plates to generate CD56+ NK cells (Figure 2). Cells were harvested and analyzed for CD56, NKp46, NKp44, NKp30, NKG2D, and KIR expression by flow cytometry. Dead cells were excluded by light-scatter profile and DRAQ7™ staining. Data shown are from representative cultures initiated with (A-E) ES (H1) cells or (F-J) iPS (STiPS-M001) cells.
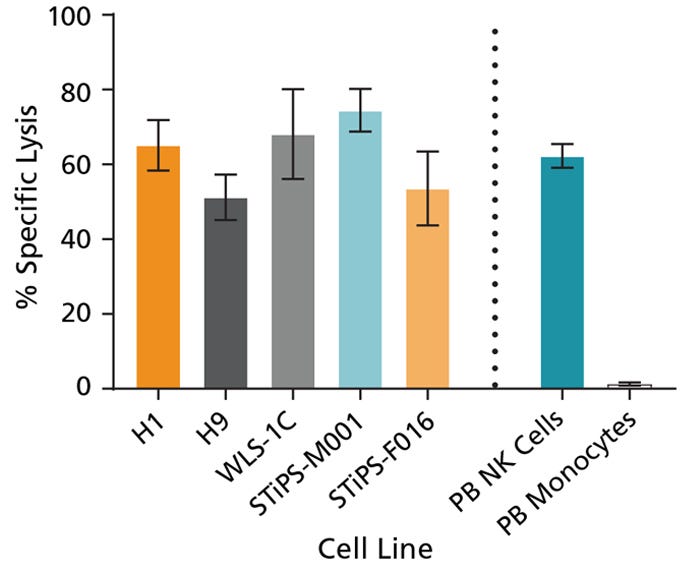
Figure 7. Cultured NK Cells Exhibit Cytotoxicity Toward K562 Cell Line
hPSC-derived CD56+ NK cells were co-cultured with calcein AM (CAM)-labeled K562 cells at a ratio of 2.5:1 for 4 hours. Isolated peripheral blood (PB) NK cells and monocytes were also co-cultured with labeled K562 cells as positive and negative controls, respectively. Before the co-culture, frozen PB NK cells were thawed and cultured overnight with StemSpan™ NK Cell Differentiation Supplement and StemSpan™ SFEM II, while PB monocytes were cultured overnight in SFEM II only. To measure maximum release, the labeled K562 cells were treated with 1% Triton™ X-100. Culture supernatants were assessed for fluorescence released by dead cells after 4 hours using a SpectraMax® microplate reader (excitation 485 nm/emission 520 nm). The % specific lysis was calculated as follows: [(test release - spontaneous release) / (maximum release - spontaneous release)] x 100%. The average specific lysis by hPSC- derived NK cells ranged between 51% and 75% as compared to 62% specific lysis by PB NK cells. Cultures of ES (H1 and H9) and iPS (WLS-1C, STiPS-M001, and STiPS-F016) cells are shown. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3 - 7).
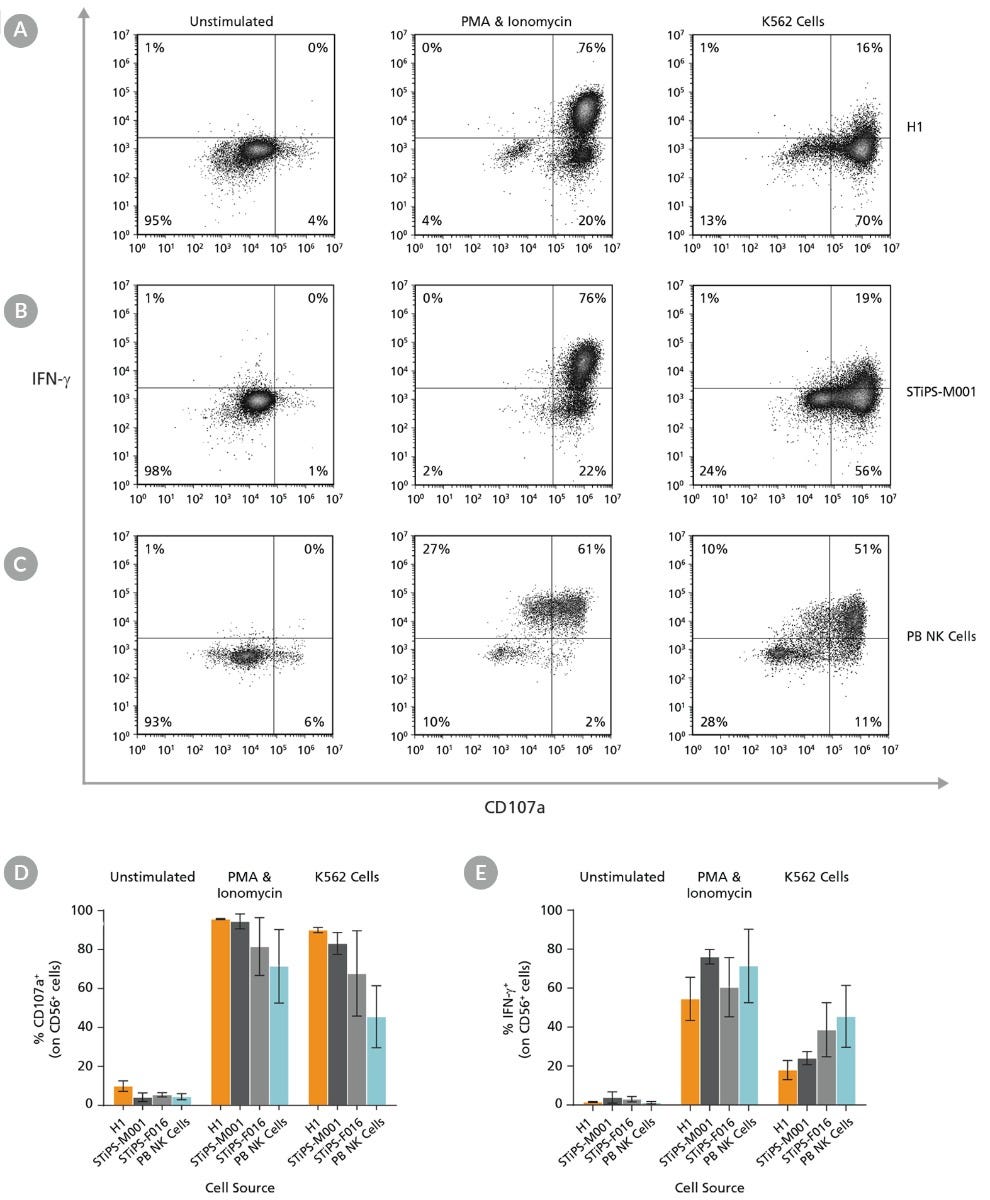
Figure 8. Cultured hPSC-Derived CD56+ NK Cells Are Induced to Express Surface CD107a and Produce IFN-γ After Co-Culture with K562 Target Cells or Stimulation with PMA and Ionomycin
hPSC-derived NK cells were obtained using STEMdiff™ NK Cell Kit as described. hPSC-derived CD56+ NK cells were left unstimulated or were stimulated with either phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and ionomycin or with K562 cells at a ratio of 1:1 effector to target cells. CD107a antibody and stimulation factors were added to each well. After one hour, monensin and brefeldin A were added to each well to inhibit protein transport. After a total incubation time of 4 hours at 37°C, cells were washed and stained with Zombie NIR™ Fixable Viability Kit and CD56. Cells were then fixed, permeabilized, and stained for IFN-γ. Surface CD107a and intracellular IFN-γ expression were assessed using flow cytometry. Representative samples are gated on CD56. (A) Representative unstimulated, PMA & ionomycin- stimulated, and K562-stimulated ES (H1) cell-derived NK cell samples. (B) Representative unstimulated, PMA & ionomycin-stimulated, and K562-stimulated iPS (STiPS-M001) cell-derived NK cell samples. (C) Representative unstimulated, PMA & ionomycin-stimulated, and K562-stimulated PB NK cell samples. The PB NK cell sample was thawed and cultured overnight in StemSpan™ SFEM II supplemented with IL-2 prior to this assay. (D) Summary of CD107a and (E) IFN-γ expression results by NK cells. Upon stimulation, hPSC-derived CD56+ NK cells are able to degranulate, as shown by surface expression of CD107a (average range: 82 - 96% for PMA & ionomycin stimulation and 68 - 90% for K562 stimulation) and secrete IFN-γ (54 - 76% and 18 - 39% for PMA & ionomycin and K562 stimulation, respectively). Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 2 - 4 ).
请在《产品说明书》中查找相关支持信息和使用说明,或浏览下方更多实验方案。
本产品专为以下研究领域设计,适用于工作流程中的高亮阶段。探索这些工作流程,了解更多我们为各研究领域提供的其他配套产品。
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
| 物种 | 人类 |
|---|---|
| 配方 | 无血清 |
用于将人多能干细胞(hPSCs)分化为单核细胞
用于人CD34+细胞扩增及分化为淋系祖细胞的添加物

用于淋系祖细胞扩增与分化的包板材料

用于淋系祖细胞向NK细胞分化的添加物

用于生成拟胚体的无血清培养基,以支持下游淋系分化
无动物成分培养补充剂,用于中胚层定向分化并具备下游淋系分化潜能
无动物成分培养补充剂,专为淋系潜能造血分化而优化
用于hPSC向T细胞的扩增和分化
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。
在线联系