产品号 #100-0074_C
用于将人 ES 细胞或 iPS 细胞分化为红系祖细胞
若您需要咨询产品或有任何技术问题,请通过官方电话 400 885 9050 或邮箱 info.cn@stemcell.com 与我们联系。
用于将人 ES 细胞或 iPS 细胞分化为红系祖细胞
用于将人 ES 细胞或 iPS 细胞分化为红系祖细胞
STEMdiff™ 红系分化试剂盒专为在无血清、无饲养细胞条件下,将人胚胎干细胞(ES细胞)和诱导多能干细胞(iPS细胞)分化为红系前体细胞(红细胞祖细胞)而设计。这些细胞表达 Glycophorin A 和 CD71。该试剂盒采用简便的二维(2D)分化方案,分为两个阶段进行:
第一阶段(第0–12天):向基础培养基中依次添加 STEMdiff™ 造血补充剂A 和红系补充剂E1,以诱导细胞向红系倾向的造血祖细胞方向分化。此阶段结束时,可轻松从培养上清中收集造血祖细胞。
第二阶段(第10–24天):通过添加红系补充剂E2 和 StemSpan™ SFEM II,对细胞进一步分化为红系前体细胞。在这一14天的红系分化阶段,细胞平均扩增241倍(±190倍,95%置信区间),第24天的细胞群体中通常含有约74%(±5%,95%置信区间)的 CD71⁺GlyA⁺ 红细胞母细胞。
使用 STEMdiff™ 红系分化试剂盒生成的细胞在适当的成熟培养条件下,还可进一步分化为晚幼红细胞(normoblasts)和网织红细胞(reticulocytes)。该试剂盒已针对以下细胞维持体系进行优化:mTeSR™1(目录号 #85850)、mTeSR™ Plus(目录号 #100-0276)和 TeSR™-E8™(目录号 #05990)。
分类
专用培养基
细胞类型
红系细胞,造血干/祖细胞
种属
人
应用
细胞培养,分化,扩增
品牌
STEMdiff
研究领域
疾病建模,药物发现和毒理检测,干细胞生物学,移植研究
制剂类别
无血清
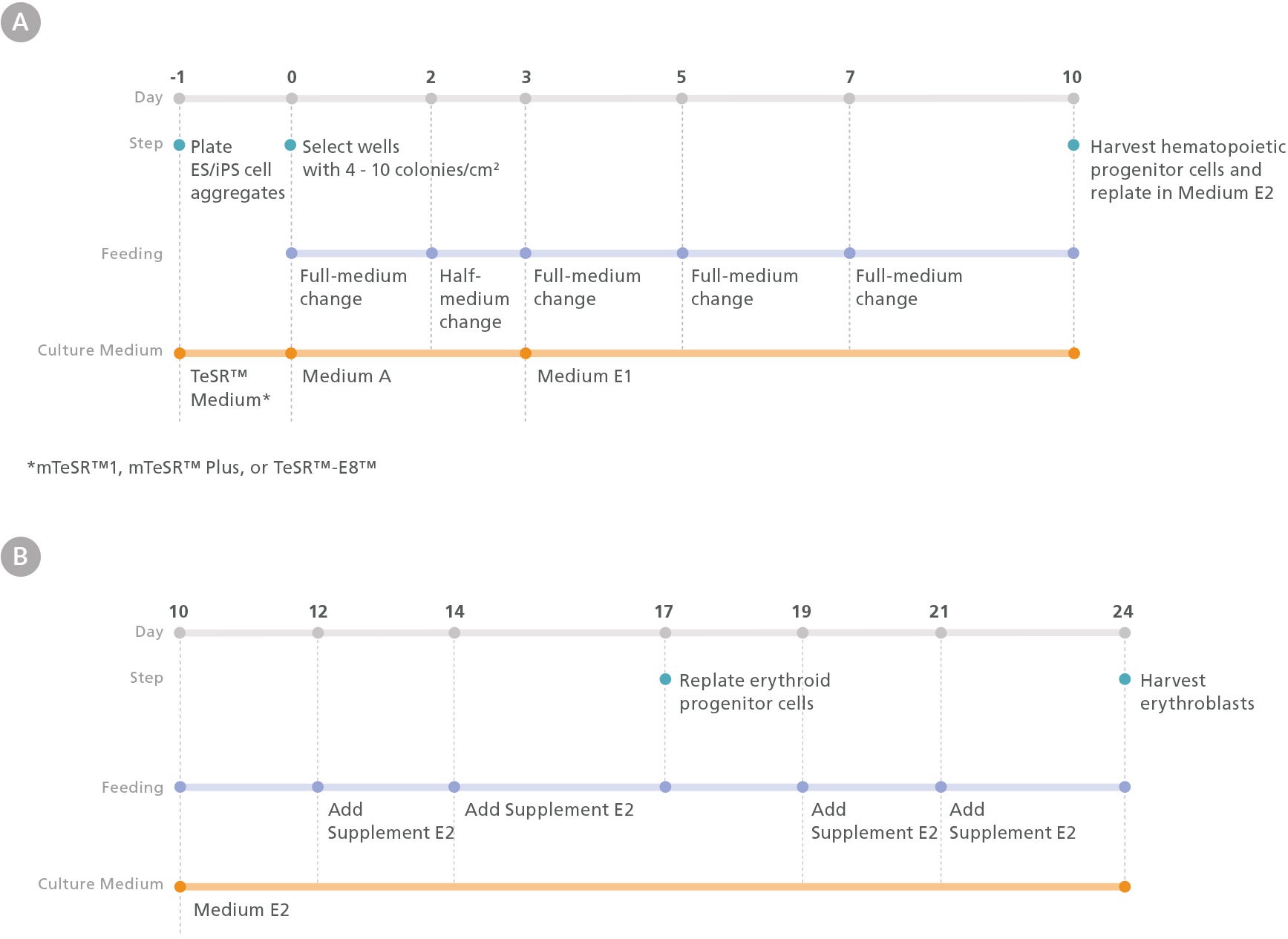
Figure 1. Erythroid Differentiation Protocol
The protocol involves two main steps: (A) hematopoietic specification of human embryonic stem (hES) or induced pluripotent stem (hiPS) cells and (B) differentiation of hES or hiPS cell-derived HPCs into erythroid cells. One day prior to differentiation, hES or hiPS cells were plated as small aggregates (100 - 200 µm diameter) at a density of 15 - 20 aggregates/cm2 in mTeSR™1, mTeSR™ Plus, or TeSR™-E8™ medium on Corning® Matrigel®-coated plates. After attaching overnight, mesoderm differentiation was initiated by changing the medium to Medium A (STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Basal Medium + STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Supplement A). On day 3, the medium was changed to Medium E1 (STEMdiff™ Hematopoietic Basal Medium + STEMdiff™ Erythroid Supplement E1) to induce hematoendothelial and hematopoietic specification. On day 10, hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) in suspension were harvested from the culture and counted. Following this, HPCs were replated in Medium E2 (StemSpan™ SFEM II + STEMdiff™ Erythroid Supplement E2) at a density of 4 x 10 4 cells/mL and cultured for 14 days to generate erythroblasts.
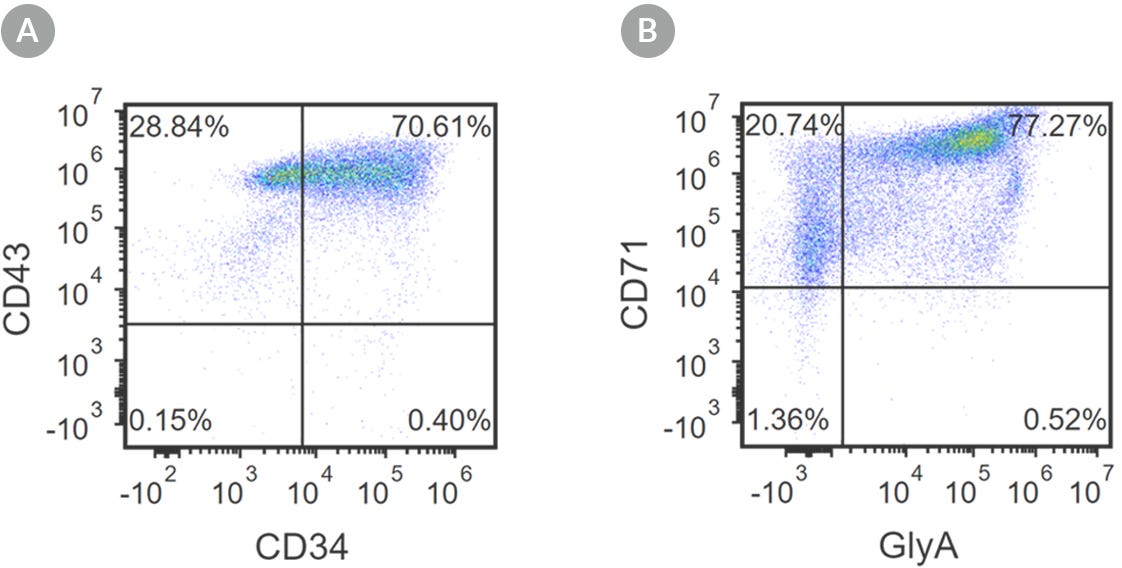
Figure 2. Robust and Efficient Generation of CD71+GlyA+ Erythroids Using STEMdiff™ Erythroid Kit
hES and hiPS cells were induced to differentiate into CD71+GlyA+ cells using the 24-day protocol shown in Figure 1. Following the initial 10-day culture period and at the end of the 24-day protocol, cells were harvested from the supernatant and analyzed by flow cytometry. Dead cells were excluded by light scatter profile and propidium iodide staining. (A) Representative flow cytometry plot for iPSC-derived (1C) cells analyzed on day 10. Cells were identified as CD34+CD43+ hematopoietic progenitors. (B) After 24 days of culture, cells were identified as having differentiated into CD71+ GlyA+ erythroblasts. The erythroid identity of the generated cells was additionally assessed by cell morphology and hemoglobin expression (see Figure 4).
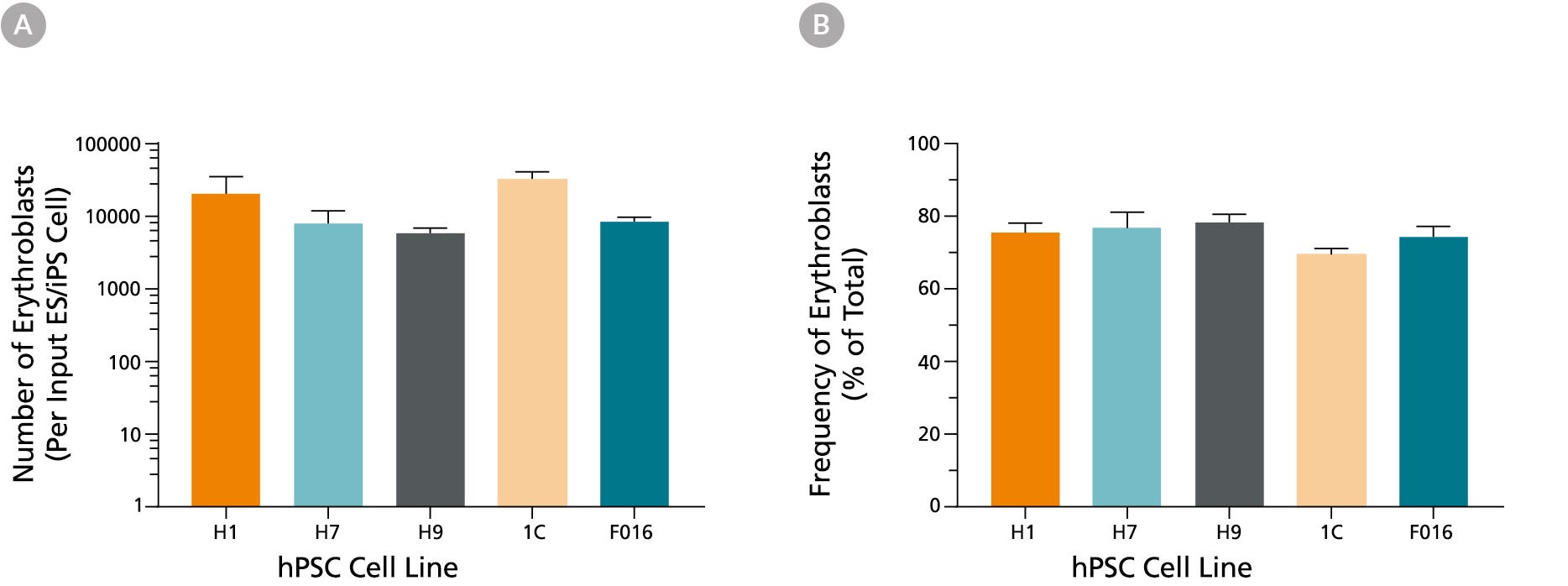
Figure 3. Production of Erythroid Cells from hES and hiPS cells After 24 Days of Culture in the STEMdiff™ Erythroid Kit
(A) Shown are the average numbers of viable, GlyA+ erythroid cells generated per input cell after culturing hES and hiPS cells for 24 days using the STEMdiff™ Erythroid Kit. (B) The overall frequency of GlyA+ erythroid cells present in culture after 24 days is shown as a percentage of total nucleated cells present. Data are presented as mean and SEM (n = 5 - 21) for six individual hES and hiPS cell lines.
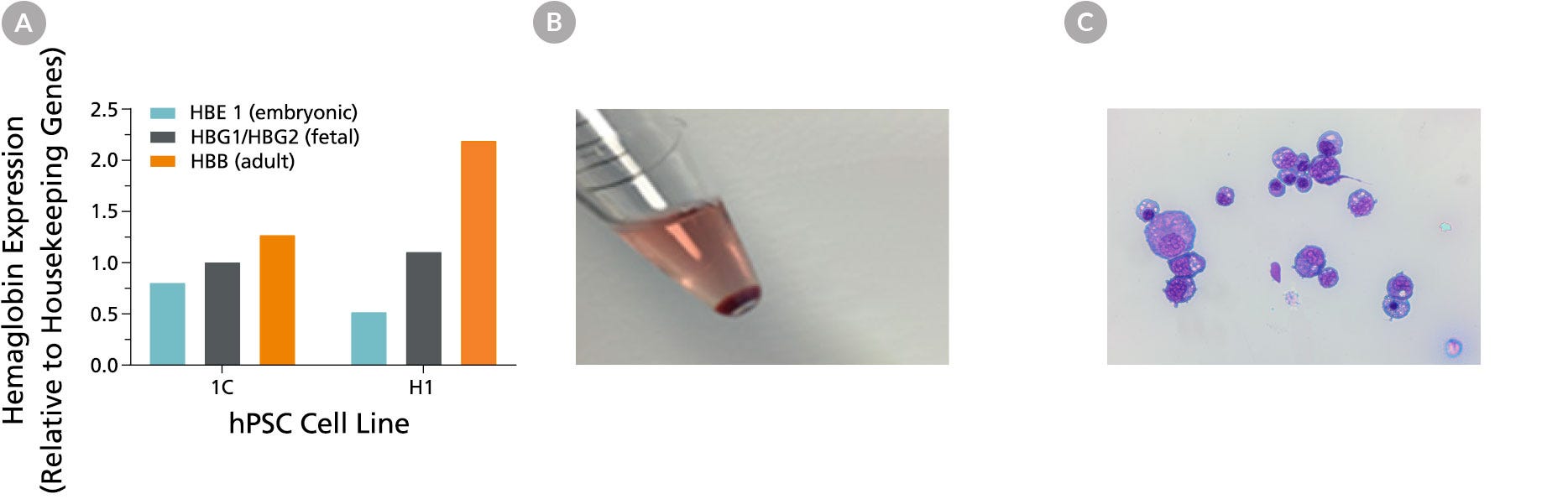

Figure 4. hES and hiPS cells-Derived Erythroid Cells Are Hemoglobinized and Display Typical Erythroid Morphology
(A) Erythroid cells generated with the STEMdiff™ Erythroid Kit express a mix of primitive (embryonic) and definitive (fetal, adult) hemoglobin. Shown are the results of qPCR analysis for globin gene expression after 24 days of culture. (B) A picture of the cell pellet shows that cells produced in culture are hemoglobinized. (C) Cells display typical basophilic erythroblast morphology after 24 days of culture using the STEMdiff™ Erythroid Kit (40X magnification, May-Grunwald Giemsa stain).
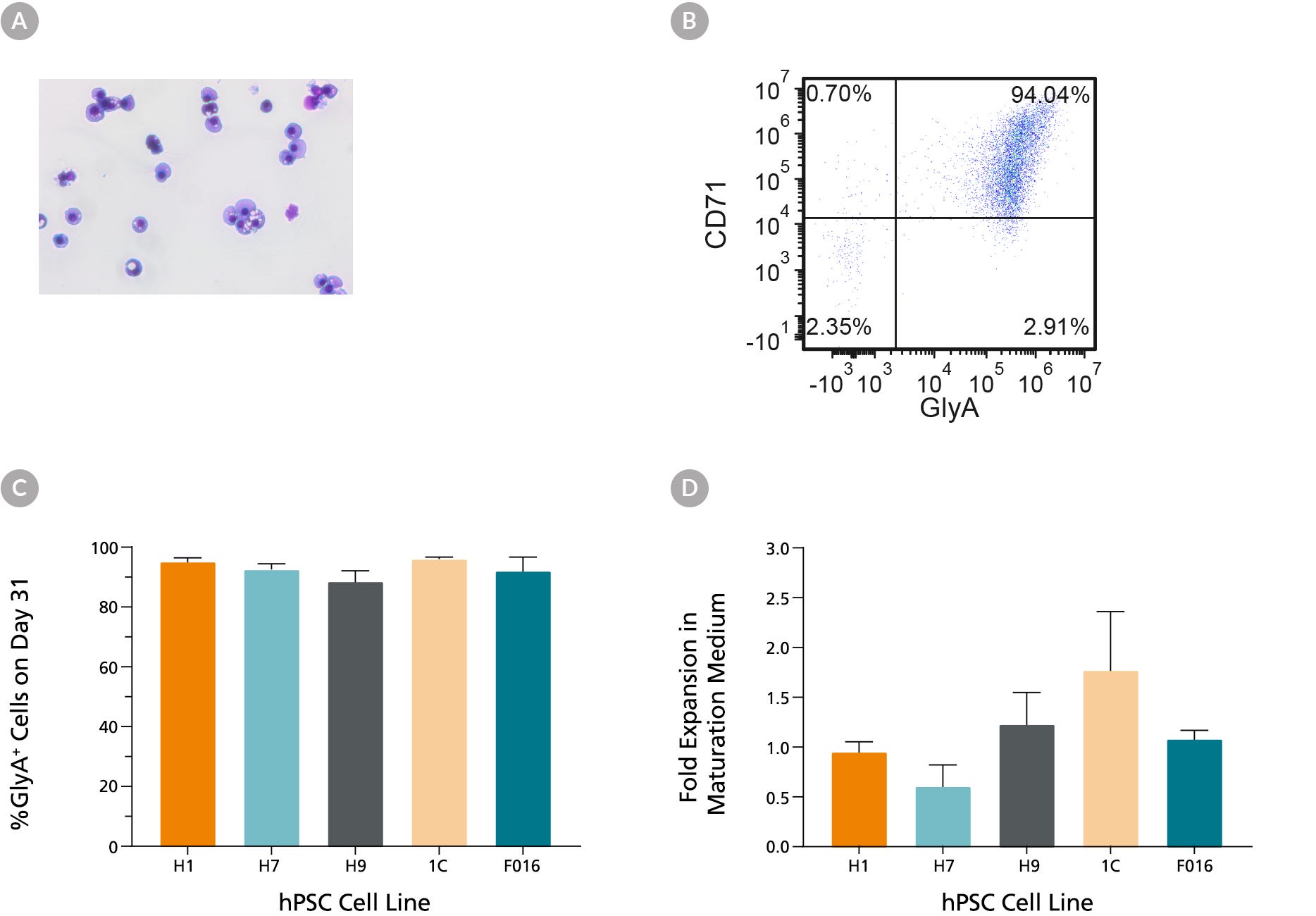
Figure 5. hES and hiPS Cell-Derived Erythroid Cells Can Mature into CD71low/GlyA+ Normoblasts
hES and hiPS cell-derived erythroblasts can mature further when cultured for an additional 7 days in maturation conditions (StemSpan™ SFEM II medium with human serum (3%) and EPO (3 U/mL)). (A) Further maturation of the erythroid cells results in smaller cells with condensed nuclei, which is typical for orthochromatic normoblasts (40X magnification, May-Grunwald Giemsa stain). (B) A representative flow cytometry plot shows that over 90% of the cells are GlyA+ and majority of cells have decreased CD71 expression, which is consistent with erythroid maturation. (C) Bar graphs summarize the average frequencies of GlyA+ erythroid cells on day 31 across all 6 hiPS cell lines. (D) Notably, fold expansion data shows that cell numbers are maintained during the maturation culture. Data are presented as mean and SEM (n=2-6).
请在《产品说明书》中查找相关支持信息和使用说明,或浏览下方更多实验方案。
本产品专为以下研究领域设计,适用于工作流程中的高亮阶段。探索这些工作流程,了解更多我们为各研究领域提供的其他配套产品。
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
| 物种 | 人类 |
|---|---|
| 配方 | 无血清 |
用于将人ES细胞或iPS细胞分化为造血祖细胞

无饲养层、无动物成分的人胚胎干细胞和诱导多能干细胞维持培养基

<p>cGMP标准、无饲养层的hESC和iPSC维持培养基</p>
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。
在线联系