产品号 #05145_C
用于长期维持 hPSC 衍生的人类肠道类器官的无血清培养基
若您需要咨询产品或有任何技术问题,请通过官方电话 400 885 9050 或邮箱 info.cn@stemcell.com 与我们联系。
用于长期维持 hPSC 衍生的人类肠道类器官的无血清培养基
用于长期维持 hPSC 衍生的人类肠道类器官的无血清培养基
长期保存人肠道类器官,将其作为肠道研究、疾病建模、药物研发和化合物筛选的模型系统。使用无血清 STEMdiff™ 肠道类器官生长培养基 (OGM),可长期稳定地培养源自人类多能干细胞 (hPSC) 的肠道类器官。
细胞类型
内胚层,PSC衍生,肠道细胞
种属
人
应用
细胞培养,分化,类器官培养
品牌
STEMdiff
研究领域
疾病建模,药物发现和毒理检测,上皮细胞研究
制剂类别
无血清
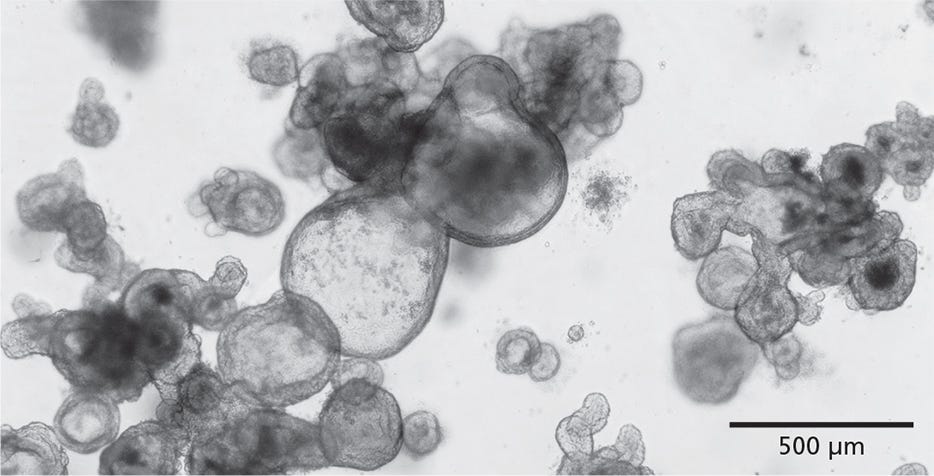
Figure 1. STEMdiff™ Intestinal Organoid Kit Enables the Growth of Intestinal Organoids from PSCs
STEMdiff™ Intestinal Organoid Kit facilitates directed differentiation of PSCs to form human small intestinal organoids. The organoids exhibit a polarized epithelial monolayer surrounding a hollow lumen and are associated with a mesenchymal cell population. Pictured are passage 3 human intestinal organoids generated using this kit.
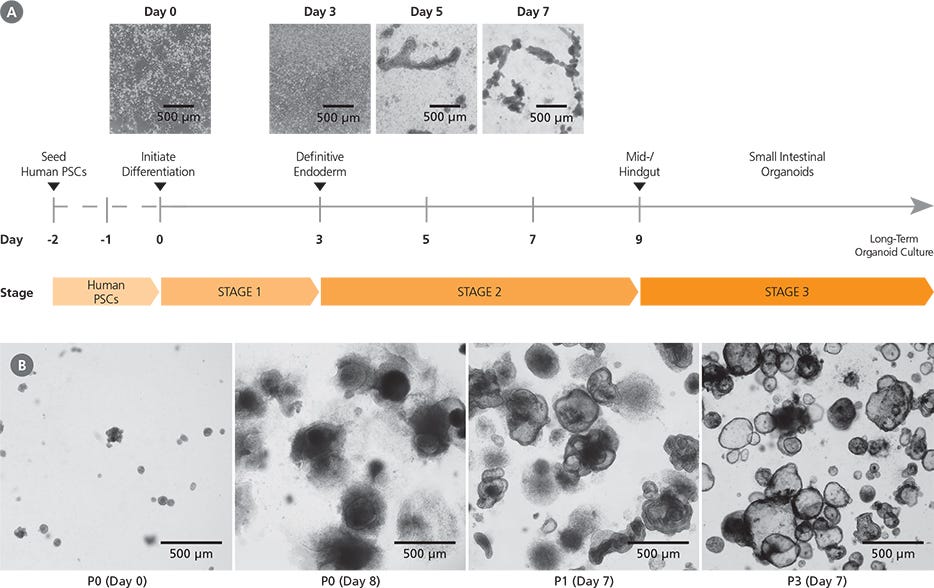
Figure 2. Generation of Human Intestinal Organoid Cultures Using the STEMdiff™ Intestinal Organoid Kit
(A) Human PSC cultures progress through a three-stage differentiation process to generate human intestinal organoids. By day 3 of the protocol, cultures exhibit characteristics typical of definitive endoderm and mid-/hindgut differentiation is initiated. During mid-/hindgut differentiation (days 5 - 9), cells form mid-/hindgut spheroids that are released from the cell monolayer into the culture medium. These spheroids are collected and embedded in extracellular matrix. (B) Embedded mid-/hindgut spheroids cultured in STEMdiff™ Intestinal Organoid Growth Medium mature into intestinal organoids (days in parentheses indicate days post-embedding in a given passage). Once established, intestinal organoids can be maintained and expanded in culture by passaging every 7 - 10 days. After multiple passages, the organoids generally exhibit less sinking within the matrix dome and a lower proportion of mesenchymal cells.
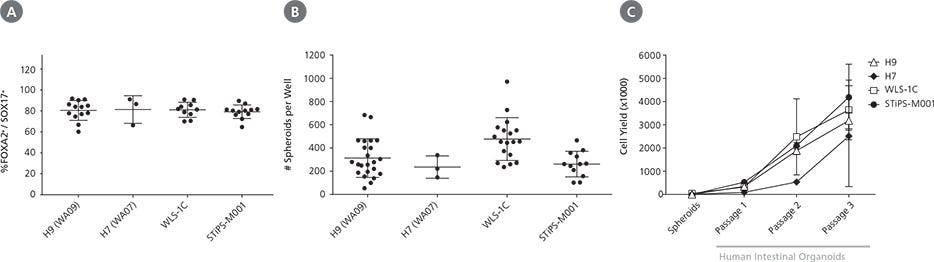
Figure 3. STEMdiff™ Intestinal Organoid Kit Supports Robust Differentiation and Expansion Across ESC and iPSC Lines
STEMdiff™ Intestinal Organoid Kit enables high-efficiency generation of intestinal organoids from both ESCs (H9, H7) and iPSCs (WLS-1C, STiPS-MOO1). (A) Organoids initiated from a variety of cell lines show efficient induction of definitive endoderm, measured by co-expression of FOXA2 and SOX17 on day 3 of differentiation. (B) Both ESCand iPSC-derived cultures demonstrate efficient spheroid formation upon mid-/hindgut induction. The total number of spheroids obtained per well in a given differentiation is shown. (C) Organoids cultured from either ESCs or iPSCs can be expanded and maintained over multiple passages. Shown is the total cell yield per passage. Organoids were passaged every 7 - 10 days with a split ratio between 1 in 2 and 1 in 4. Data points represent the mean of 3 biological replicates. Error bars throughout represent standard deviation of the mean.
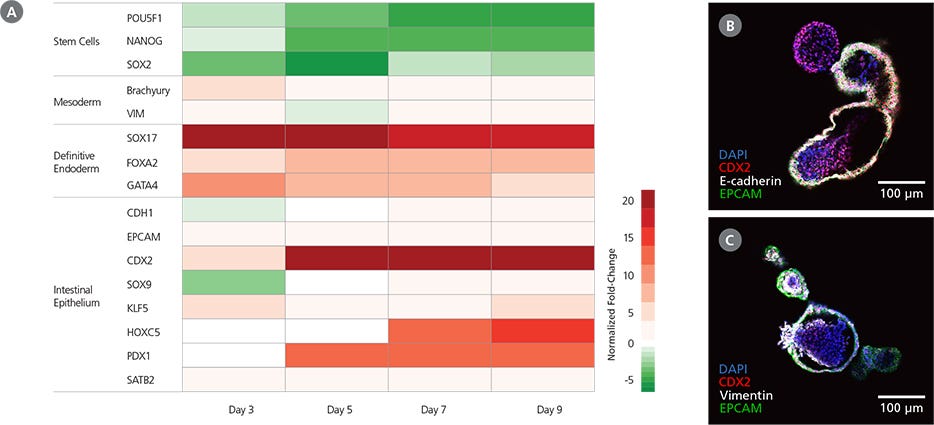
Figure 4. Characteristics of Mid-/Hindgut Spheroids Generated with STEMdiff™ Intestinal Organoid Kit
(A) Cultures differentiated using STEMdiff™ Intestinal Organoid Kit exhibit the expected markers during definitive endoderm and mid-/hindgut specification. During the protocol, gene expression patterns shift from pluripotency markers (day 0) to definitive endoderm markers by day 3 and those of the mid-/hindgut epithelium by day 9. Mid-/hindgut cultures (day 9) also express markers of the associated mesenchyme. Marker levels were assessed by RT-qPCR and normalized to expression levels for undifferentiatied H9 cells. (B) Mid-/hindgut spheroids (day 9) express markers of the intestinal epithelium (CDX2, E-cadherin, EPCAM). (C) Mid-/hindgut spheroids (day 9) also incorporate components of the associated mesenchyme (vimentin).
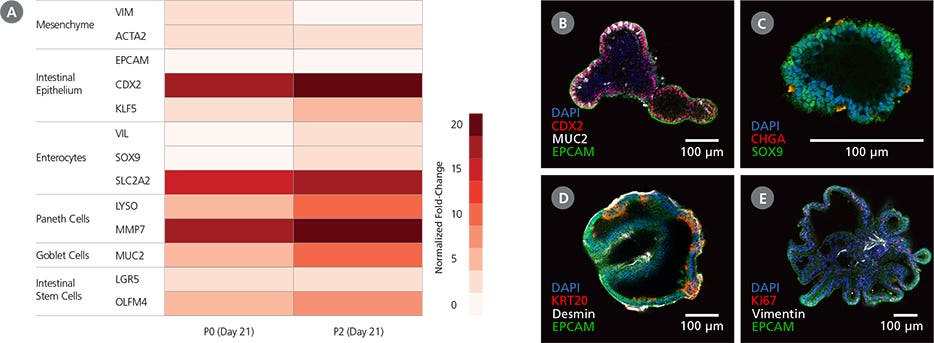
Figure 5. Intestinal Organoids Cultured In STEMdiff™ Intestinal Organoid Growth Medium Exhibit Features of the Intestinal Epithelium
(A) Differentiated PSC-derived intestinal organoids express markers of the intestinal epithelium and the associated mesenchyme. Marker levels were assessed by RT-qPCR and normalized to expression levels for undifferentiated H9 cells. (B,C) Intestinal organoids express markers of intestinal progenitor cells including CDX2 and the intestinal crypt marker SOX9. The organoids are composed of a polarized epithelium, visualized by the localization of EPCAM to the exterior (basolateral) surface of the organoids (B), and express markers typical of mature cell types including MUC2 (B: goblet cells) and CHGA (C: enteroendocrine cells). (D,E) Observation of desmin (D) and vimentin (E) in intestinal organoids demonstrates incorporation of mesenchymal cells in the organoid cultures, while KRT20 (D) and Ki67 (E) are markers of differentiated intestinal cells and putative intestinal stem cells, respectively. Images are digital cross-sections of whole-mount immunofluorescence-stained intestinal organoids at P28 (Day 7).
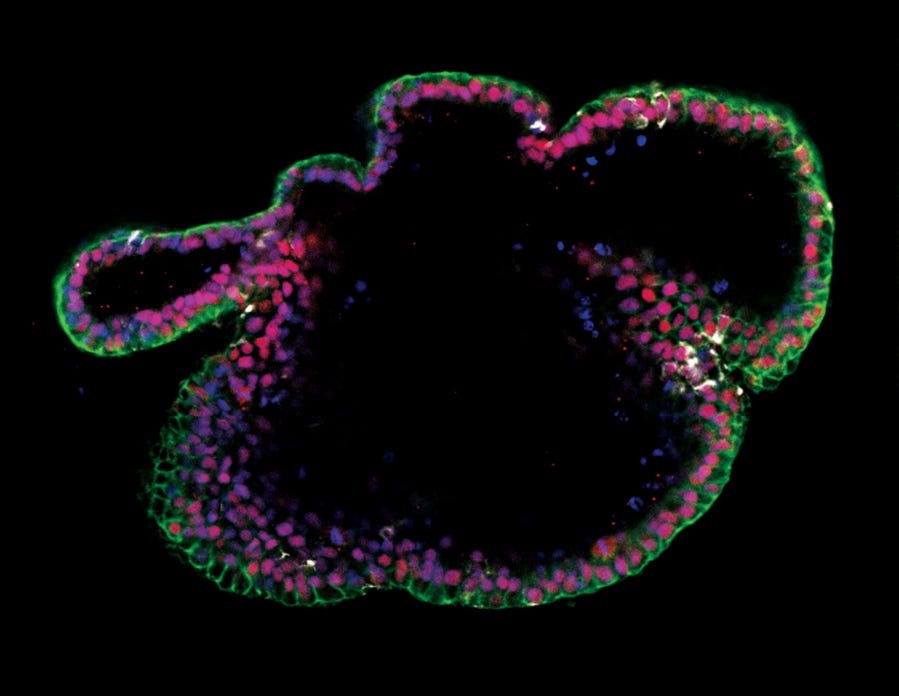
Figure 6. Generation of Intestinal Organoids from hPSCs Maintained in mTeSR™ Plus
Human ES (H9) cells were cultured with mTeSR™ Plus and directed to intestinal organoids using the STEMdiff™ Intestinal Organoid Kit. Image shows markers of the intestinal epithelium EpCAM (green) and CDX2 (red), and intestinal mesenchyme marker vimentin (white). Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue).
请在《产品说明书》中查找相关支持信息和使用说明,或浏览下方更多实验方案。
本产品专为以下研究领域设计,适用于工作流程中的高亮阶段。探索这些工作流程,了解更多我们为各研究领域提供的其他配套产品。
Thank you for your interest in IntestiCult™ Organoid Growth Medium (Human). Please provide us with your contact information and your local representative will contact you with a customized quote. Where appropriate, they can also assist you with a(n):
Estimated delivery time for your area
Product sample or exclusive offer
In-lab demonstration
| 物种 | 人类 |
|---|---|
| 配方 | 无血清 |
<p>用于将人胚胎干细胞(hESCs)和人诱导多能干细胞(iPSCs)分化为确定性内胚层的定义明确、无动物源成分的培养基</p>
<p>人胚胎干细胞和iPS细胞向胰腺祖细胞分化的无血清培养基</p>
用于建立和维持小鼠肠道类器官的培养基
用于建立和维持人肠道类器官的培养基
法律声明:
STEMdiff™ Intestinal Organoid Kit was developed under license to intellectual property owned by the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital.
质量保证:
产品仅供研究使用,不用于针对人或动物的诊断或治疗。 欲获悉更多关于STEMCELL的质控信息,请访问 STEMCELL.CN/COMPLIANCE.
Safety Statement:
CA WARNING: This product can expose you to Progesterone which is known to the State of California to cause cancer. For more information go to www.P65Warnings.ca.gov
扫描二维码或搜索微信号STEMCELLTech,即可关注我们的微信平台,第一时间接收丰富的技术资源和最新的活动信息。
如您有任何问题,欢迎发消息给STEMCELLTech微信公众平台,或与我们通过电话/邮件联系:400 885 9050 INFO.CN@STEMCELL.COM。
在线联系